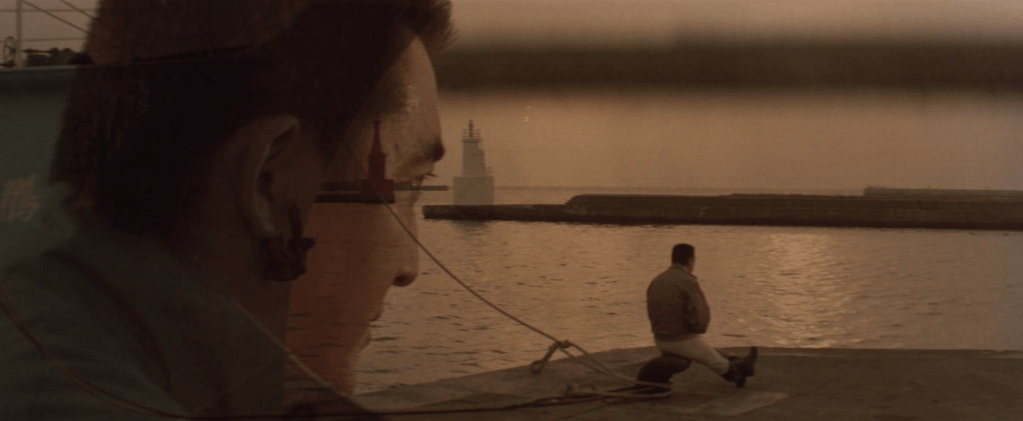
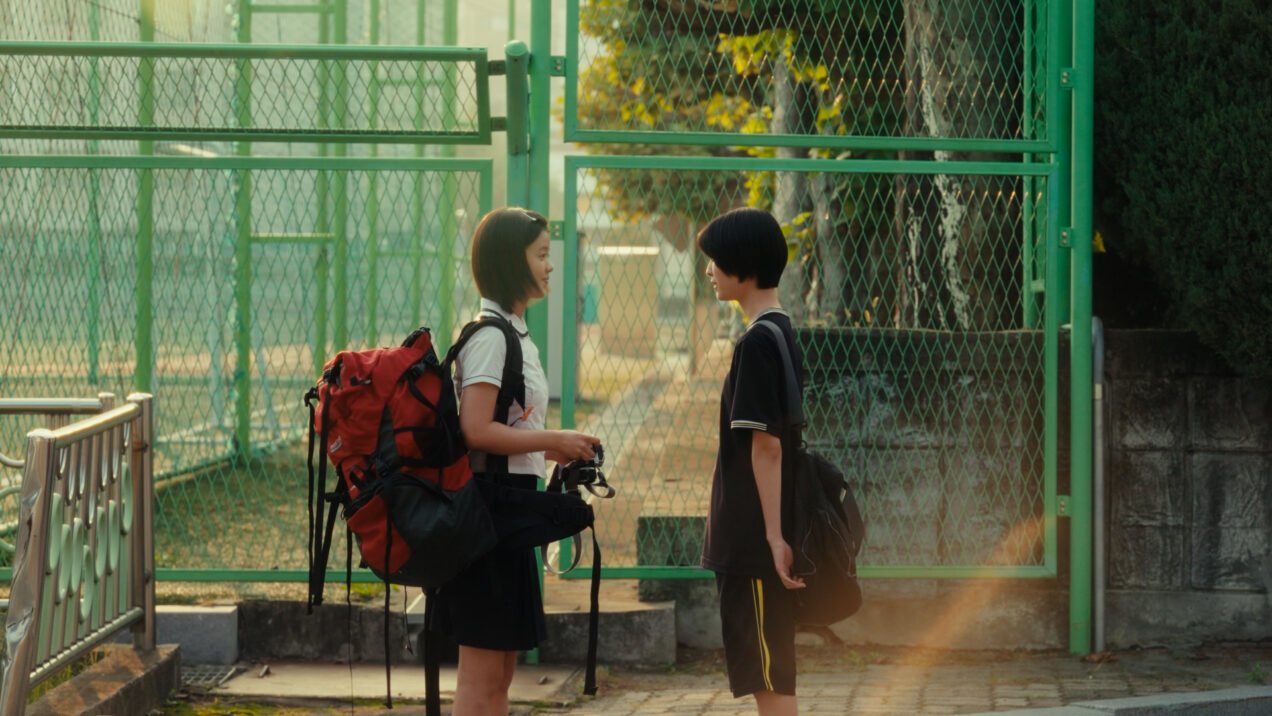Myagmar (Tuvshinbayar Amartuvshin) asks a teenage monk if he thinks atonement is possible. The monk, Sodoo, tells him that he thinks it is, but that it’s difficult and not many people can achieve it. The irony of Myagmar’s life is that he becomes a kind of ferryman, delivering the deceased to a kind of liberation he will never find while trapped in the eternal hell of Ulaanbaatar. Much less upbeat than his previous film, The Sales Girl, Sengedorj Janchivdorj’s melancholy character study finds its solitary hero consumed alternately by guilt and rage while trapped within a world of constant unfairness and inequality.
As Myagmar tries to explain, he’s not disabled, merely nervous though his stammer turns out to stem from extensive beatings during the 14 years he spent in “Dad’s house”, or prison, that have left him with brain damage and the melancholy stillness of one already dead. As he tells the friendly coffin maker at the funeral home where he is eventually employed as a hearse driver, he applied for countless other jobs but no one would give him one because of his criminal record and outsider status. Having lost his only living relative in his mother who died while he was inside, Myagmar lives alone with a pack of stray dogs that he’s taken in and cares for. He explains to the coffin maker’s daughter Saruul (Narantsetseg Ganbaatar) that some of them probably had families, but were abandoned because they got old or they were sick and it costs too much to care for a sick dog. Mostly though, they’re strays, like him, with no home or place to belong.
Myagmar extends this same kindness to Saruul having become captivated by her on seeing her come to collect her father from work. Coffin maker Sodnom thinks she’s a medical student, but Myagmar soon discovers that she works in the seedy underbelly of Ulaanbataar’s sex industry and is also at the centre of a political scandal involving a leaked tape of a politician said to have been uploaded by the woman herself as a last resort and means of revenge with a personal rather than political motivation. Myagmar follows Saruul around in a way which might seem creepy, but is emblematic of his shyness and lack of confidence in himself. Though Saruul eventually responds to his kindness and begins to return some of his affection, it’s largely because they recognise each other as two people who are trapped in this unending hell, he in his sense of futility and the trauma of his incarceration, and she within sex work and abuse.
At a particularly low point, Saruul tells Myagmar that she wants to go to “that place”, the hell that haunts him though he no longer dreams. He tells her that it is not somewhere she wants to go, that there is no light there, no day and no night. It is a living death in which even his name was taken from him and replaced by a number, as Suruul’s will also be in a moment of grim irony. But all it seems to do is reinforce the fact that this is not so different from the life Saruul lives now. They already live in hell and there is only one means of escape. The monk, Sodoo, tells Myagmar that the best revenge is forgiveness and seeking vengeance won’t change anything, but he cannot overcome his sense of rage towards an unjust society. Still, Sodoo tells him that he did the right thing even if offers little sense of comfort to the melancholy hearse driver charged with transporting souls from this world to the next.
Sengedorj Janchivdorj lends the contemporary city a melancholy quality, a dark and lonely place peopled by the abandoned and downtrodden. Even Sodoo doesn’t quite know how old he is and marks his years by the day in which he was found. The more Myagmar begins to rebuild his life, the more he has to lose and the less it looks like he will be allowed to find happiness or the atonement he seeks for his crime. A gentle soul consumed by rage, he nevertheless has “capable hands” to which to entrust this justice and is capable of creating great beauty such as the stone lions he begins carving for the funeral home, but otherwise maintains a purgatorial existence unable to make a home for himself in a world of such constant cruelties.
Silent City Driver screens in Chicago 6th April as part of the 19th edition of Asian Pop-Up Cinema.
Trailer (English subtitles)