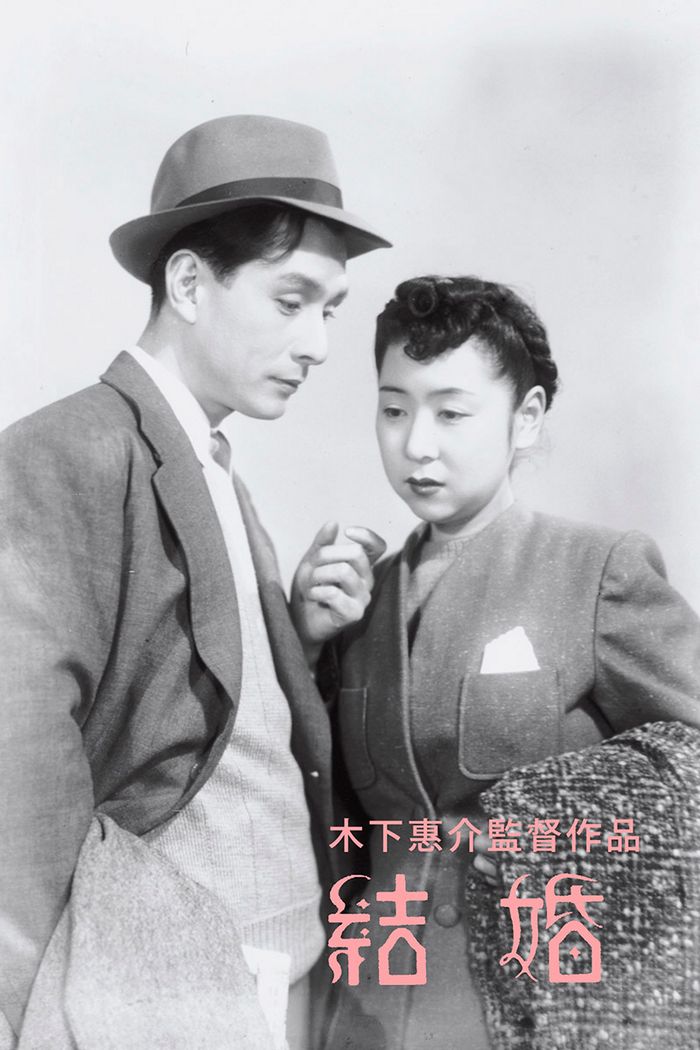
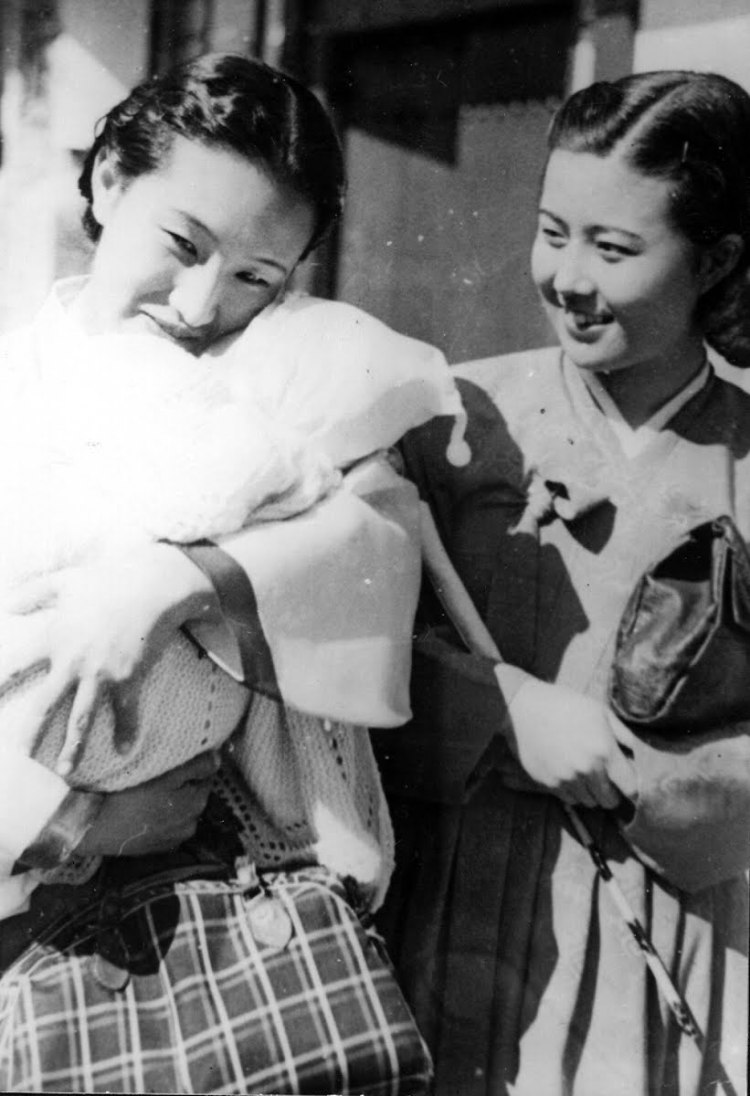
 It’s true enough that we might not have enough extant material from the pre-war and wartime eras to be as selective as some might accuse of us of being on realising that the directors we tend to remember are the ones we see as resisting. Though there were a fair few who managed simply to steer clear of the prevailing ideology, most skirted their way around the demands of the censors board by embracing the kinds of themes they could would work with. In Hideko, the Bus Conductor (秀子の車掌さん, Hideko no Shasho-san) Naruse pushes in a slightly different direction, retreating almost entirely from the troubles of the contemporary era into an idyllic vision of pastoral Japan.
It’s true enough that we might not have enough extant material from the pre-war and wartime eras to be as selective as some might accuse of us of being on realising that the directors we tend to remember are the ones we see as resisting. Though there were a fair few who managed simply to steer clear of the prevailing ideology, most skirted their way around the demands of the censors board by embracing the kinds of themes they could would work with. In Hideko, the Bus Conductor (秀子の車掌さん, Hideko no Shasho-san) Naruse pushes in a slightly different direction, retreating almost entirely from the troubles of the contemporary era into an idyllic vision of pastoral Japan.
Echoing Mr. Thank You, he opens with a POV shot of bus travelling a rural road accompanied by jaunty music. Neatly undercutting the cheerful atmosphere with ironic absurdity, we then cut to bus conductress Okoma (Hideko Takamine) announcing the next stop to an entirely empty bus. The problem is, the bus Okoma and the driver, Sonoda (Kamatari Fujiwara), operate is old, slow, and dirty. A new company, Kaihatsu, recently launched with shiny new buses that are cleaner and faster, if a little more expensive. Unsurprisingly, most people prefer to travel with Kaihatsu, meaning the only passengers waiting for Okoma’s bus are the kind that don’t have much money or are looking for different kinds of service – e.g. transporting live chickens or unusually large amounts of bags.
A radio programme recommended by her landlady gives Okoma an idea to boost business – performing as a kind of tour guide reading out interesting facts about the local area to entertain the passengers. Unfortunately, no one can quite think of any interesting facts or local landmarks in this tiny rural backwater. Nevertheless, Okoma and Sonoda are determined to give it a go, eventually obtaining permission from the decidedly laissez-faire boss who spends most of his days guzzling ramune and eating kakegori. To make sure the service is professional, they enlist the services of a local writer, Ikawa (Daijiro Natsukawa), whose notebook Okoma once returned when he left it on the bus. Weirdly, he doesn’t even want paying because he enjoys writing this kind of thing, and even coaches Okoma on how to get the cutest accent to really attract those customers with adorable local charm (even though Okoma is very proud to be thought of as nicely spoken young lady with nary an accent at all).
Of course, in true Naruse style, it’s not quite as idyllic as it seems. Most of the people we meet are poor and struggling, that’s why they’re taking this bus and not Kaihatsu’s. Even so, they’re all pleasant and polite, not even minding when Okoma asks the driver to stop by her house so she can chat with her mother, giving her a kimono she’s bought as a present (that her mum tells her off for spending her money on) and swapping her worn out cloth shoes for a classic pair of geta in which she seems to be more comfortable. At one stage, a chicken escapes from the bus and they stop to catch it, timetable be damned. Mind you, there don’t even really seem to be specific stops on this strangely occasional service. In need of passengers, Okoma and Sonoda seem content to stop and pick up random passersby who might be in search of a lift, taking them to wherever they might want to to go.
That might be one reason explaining why Okoma’s landlady is keen to warn her that she’s heard the bus company is no good, it’s just a front for some kind of unspecified shadiness. The truth, however, is more that the boss seems to be the feckless sort who enjoys being bossy but has no idea how to run a business. Distracted by Okoma’s monologue, Sonoda starts forgetting to stop and pick people up and eventually has to slam on the brakes when a child runs out into the street. While they’re checking on the kid, the bus rolls back over the verge, injuring Okoma and landing in farmland. Reassured that no-one has been “seriously” hurt (he’s not getting sued), the boss is then more worried about the insurance, seeing as it doesn’t cover him if the engine was running while they were stopped. Even though Sonoda explains that there’s no damage except maybe a scratch on the side, the boss suggests he scupper the engine and smash the windows so they can claim. They need a better bus, otherwise the company will have to close.
Earlier on, Sonoda and Okoma had joked about a popular slogan “When a country gets confused, loyal subjects appear”. Sonoda rolls his eyes a little and calls it “bombast”. They might not object to adding a bit about birds singing for the emperor’s long reign to their monologue, but it’s plain they aren’t going to go along with something they think is wrong because the boss says it’s a good idea. Sonoda is a little conflicted to begin with, talking it over with Ikawa who acts as the slightly patronising voice of city sophistication, he realises that if he follows the boss’ orders and lies he’ll not only be cheating the rest of society but himself too in doing something he knows to be immoral. Both he and Okoma vow they’ll quit rather than be forced into dishonesty, after all, says Okoma, there are plenty of other jobs (or perhaps not, in real terms, but still there is a choice). Suddenly, they feel quite cheerful, buoyed by their sense of moral righteousness.
An intervention from Ikawa saves their jobs, but this is still a Naruse film in which the world will always betray us, and so Okoma and Sonoda cheerfully continue their tour guiding business little knowing that the boss has gone bust and sold the bus. It might be going too far to say that Naruse envisages a fiery crash, a rude awakening for Okoma and Sonoda who will be left with only the cold comfort that they stood up against authoritarianism when it all goes to hell, but the subtle allegory is all but unmissable. Absurdly cheerful, and just a little bit depressing if you stop to think about it, Hideko the Bus Conductor is a charming jaunt through rural ‘40s Japan filled with salt of the earth types just trying to muddle through while the big bosses put their feet up and pop ramune marbles all day long without a care in the world.
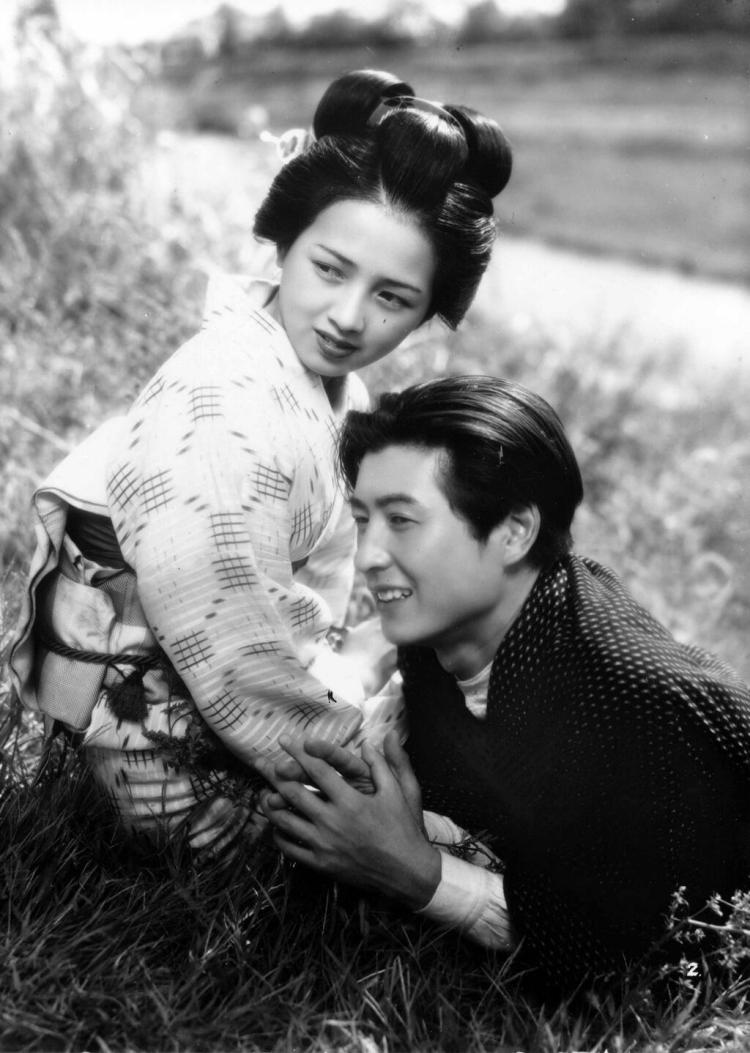
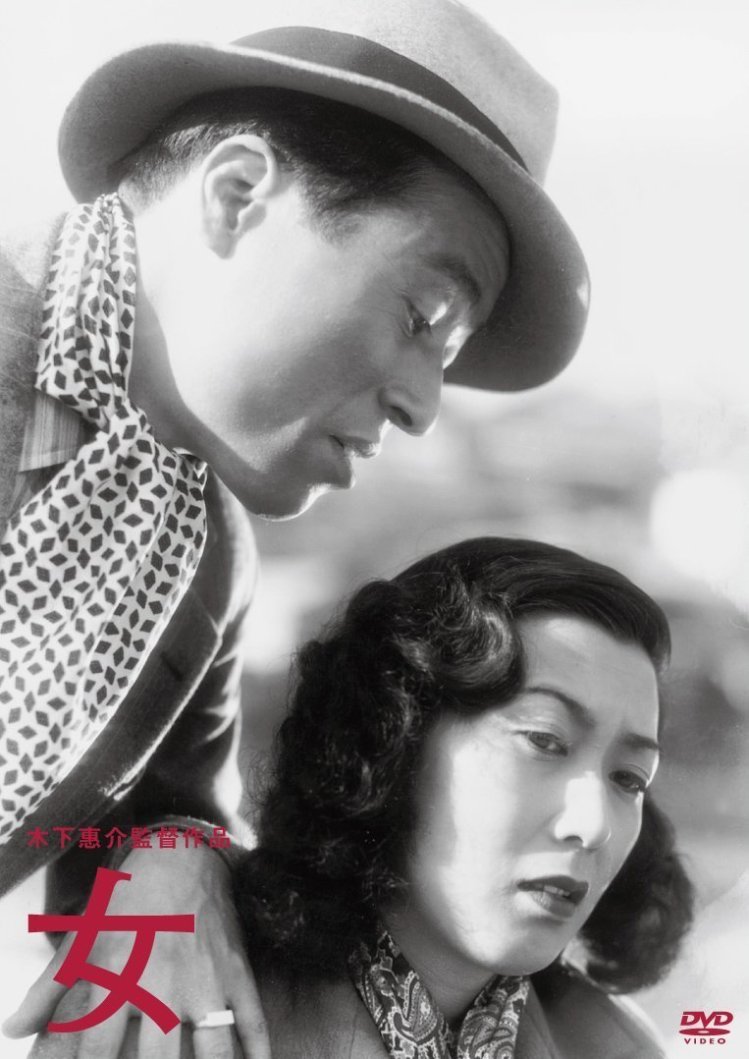












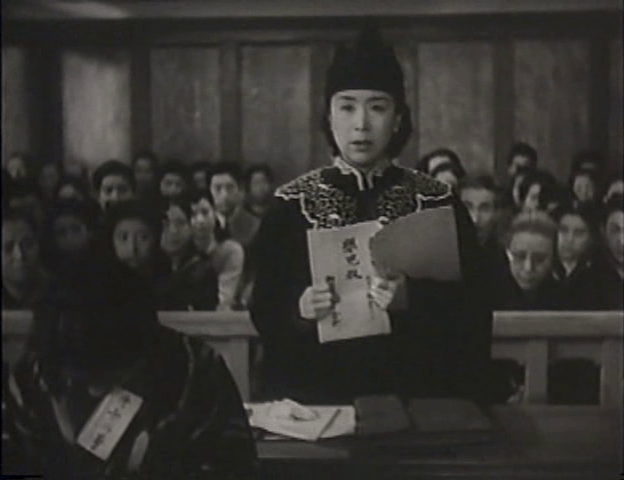 Female suffering in an oppressive society had always been at the forefront of Mizoguchi’s filmmaking even if he, like many of his contemporaries, found his aims frustrated by the increasingly censorious militarist regime. In some senses, the early days of occupation may not have been much better as one form of propaganda was essentially substituted for another if one that most would find more palatable. The first of his “women’s liberation trilogy”, Victory of Women (女性の勝利,
Female suffering in an oppressive society had always been at the forefront of Mizoguchi’s filmmaking even if he, like many of his contemporaries, found his aims frustrated by the increasingly censorious militarist regime. In some senses, the early days of occupation may not have been much better as one form of propaganda was essentially substituted for another if one that most would find more palatable. The first of his “women’s liberation trilogy”, Victory of Women (女性の勝利, 




