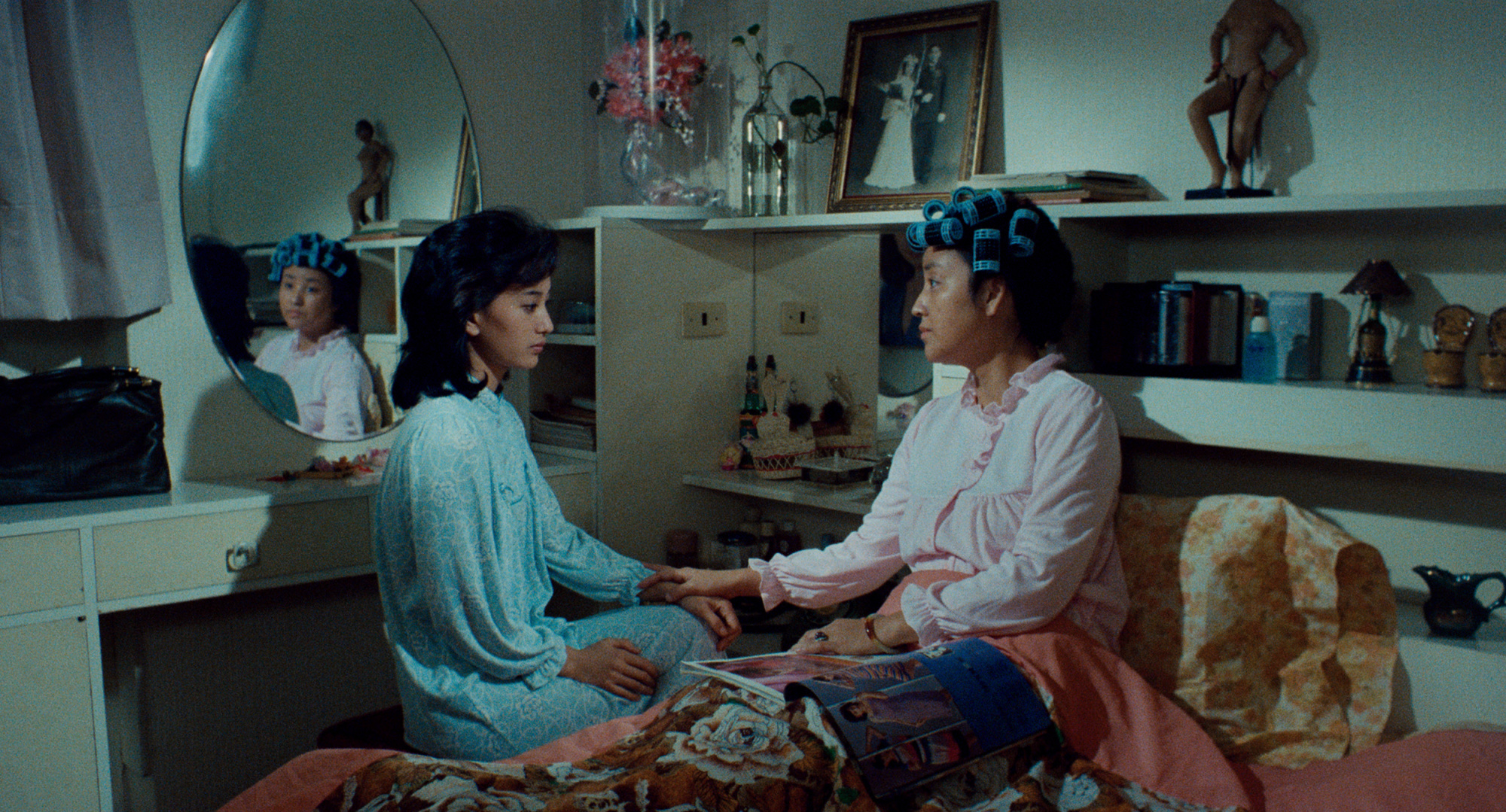
A few minutes into Wan Jen’s familial melodrama Ah Fei (油麻菜籽, yóu má càizǐ), a mother takes her children by the hand and walks to the end of a long jetty. We get the sense that she means jump and take her children with her, that she’s at the end of her tether and sees no other way out for herself, but still she thinks better of it and goes back anyway. Indeed, there isn’t really any way out for Hsin-chin, but there might be for her daughter, Ah Fei, if only Hsin-chin (Chen Chiu-yen) can bring herself to set her free.
Hsin-chin’s own mother died while she was a child and her otherwise sympathetic father later arranged her marriage to a man he thought was “honest” but turned out to be anything but. Shih-chen (Ko I-chen) is violent and irresponsible. He barely works and spends all the money Hsin-chin makes seamstressing on drink, gambling, and other women. Hsin-chin appeals to her father, but he ends up sending her back and siding with Shih-chen. He gives his son-in-law a not altogether stern talking to while encouraging him that there should at least be “civility” between husband and wife.
We can see that this patriarchal sociality trumps all. Shih-chen originally takes no interest in Ah Fei but only in his son, Ah Shong whom he takes out with him drinking and introduces to his mistress. She buys him a toy sword which both buys the boy’s affection and creates further discord in the marital home as Shih-chen conspiratorially warns him not to tell his mother how he got it. On arriving home, Shin-chen had called for Ah Shong and he had come running in without even taking his shoes off, treading mud all over the floors Ah Fei had just been washing.
Years later, Hsin-chin asks Shih-chen if he really thinks his son is as useless as he is. Shih-chen doesn’t answer, but it’s obvious that the answer is yes. These patriarchal patterns are quite obviously learned, passed down from fathers to sons in the ingrained codes of manliness. When his mother had tried to punish him when he was caught stealing bananas from a local farmer, Ah Shong turned round and said he’d tell his father her to beat her again if she didn’t stop. There is something sad and ironic in this circulation of violence as she beats her son to discipline him in much the same way her husband inflicts his violence on her and the teachers at Ah Fei’s school whack the pupils’ hands with a ruler when their grades dip below those of the previous paper. Ah Fei is studious and respectful, while Ah Shong is lazy and entitled. When his mother suffers a nasty miscarriage and calls for his help, Ah Shong doesn’t even wake up leaving Ah Fei to run alone through the night to the neighbour’s house so she can get the doctor.
While the lived in the country, Hsin-chin had cherished her daughter and remarked that there was no point raising sons while Ah Fei is the only one contributing to the family by helping her with the housework. But on their return to Taipei after Shih-chen is caught sleeping with another man’s wife and forced to pay a humiliating fine in compensation, the situation is reversed. Shih-chen appears to mellow. He now stays home painting rather than going out to philander, but is still a figure of male failure who cannot find a job to support his family and leaves the heavy lifting to an increasingly embittered Hsin-chen. Hsin-chen meanwhile concentrates all her efforts on Ah Shong and resents Ah Fei. Though the family pay 200 dollars for Ah Shong’s private school, they begrudge the 30 for Ah Fei’s extra tuition so she can get into high school. Ah Fei doesn’t even want her to finish primary education. A neighbour has heard about an opening at a local factory and Hsin-chin wants her to start right away. It’s only Shih-chen who supports her education and switches his allegiance to Ah Fei rather than Ah Song who has disappointed him. He has come realise that Ah Shong is just like him after all, and seems to have a new degree of awareness about the family’s dynamics. He doesn’t want this life for Ah Fei, while Hsin-chin actively tries to trap her within the domestic space just as she was trapped.
In a repeated motif, Hsin-chin picks up a pair of scissors but can use them only in passive aggressive bouts of counter-productive revenge such as shredding Shih-chen’s suits, chopping the heads off roses to express her frustration, and cutting Ah Fee’s hair so she can’t go back to school after finding out that she had a boyfriend. Even once Ah Fei is a grown woman with a good job in advertising that is actively supporting the family, she struggles to separate herself from her mother who continues to frustrate her love and discourage her from marrying. Some of this is her own bitterness, and some honest advice that Ah Fei’s choice of husband is the most important decision she’ll ever make. Marry a good man and she’ll have a good life. Marry badly and she’ll end up like Hsin-chin knowing nothing but suffering.
Of course, the crucial element is that Ah Fei has a choice that Hsin-chin never did. But at the same time she struggles to take it or to reject the internalised misogyny that ruled her mother’s life along with the patriarchal social codes that left her unable to leave a bad husband. She is well educated and financially independent so cannot be trapped in the same way her mother was even if her “escape” is ironically bound up with the patriarchal institution of marriage. Only on seeing her in a wedding dress does Hsin-chin finally accept her, reverting to the kind mother she had been in the countryside rather than the embittered old woman she had become in Taipei who is too afraid of her impending loneliness and the spectre of poverty to set her daughter free. Ah Fei’s liberation may speak of that of her generation, travelling from the countryside to a Taipei slum and finally a well-appointed flat in the centre of a rapidly developing city in the twilight of an authoritarian regime, but equally of the interconnected cycles of toxic masculinity, patriarchal entitlement, male failure, and internalised misogyny all seemingly dissolved in a single moment of forgiveness and acceptance.
Ah Fei screened as part of the BFI’s Myriad Voices: Reframing Taiwan New Cinema.
Trailer (Traditional Chinese / English subtitles)