Well established in Japanese cinema, the teenage romance comes with its own series of genre tropes, the barriers standing between the young lovers usually leaning towards the constraints of a conformist society, class differences, or familial disapproval if not introducing a note of inevitable tragedy in serious illness or physical threat. What the youngsters typically do not do or are actively at times prevented from doing is to begin to accept themselves for all they know that to do so may in a sense result in their exile from mainstream society. Yet this is exactly the conclusion with which Akihito Shiota’s debut feature Moonlight Whispers (月光の囁き, Gekko no Sasayaki), adapted from the manga by Masahiko Kikuni, eventually presents us as the teens come to embrace their unconventional relationship while accepting that others may never truly understand.
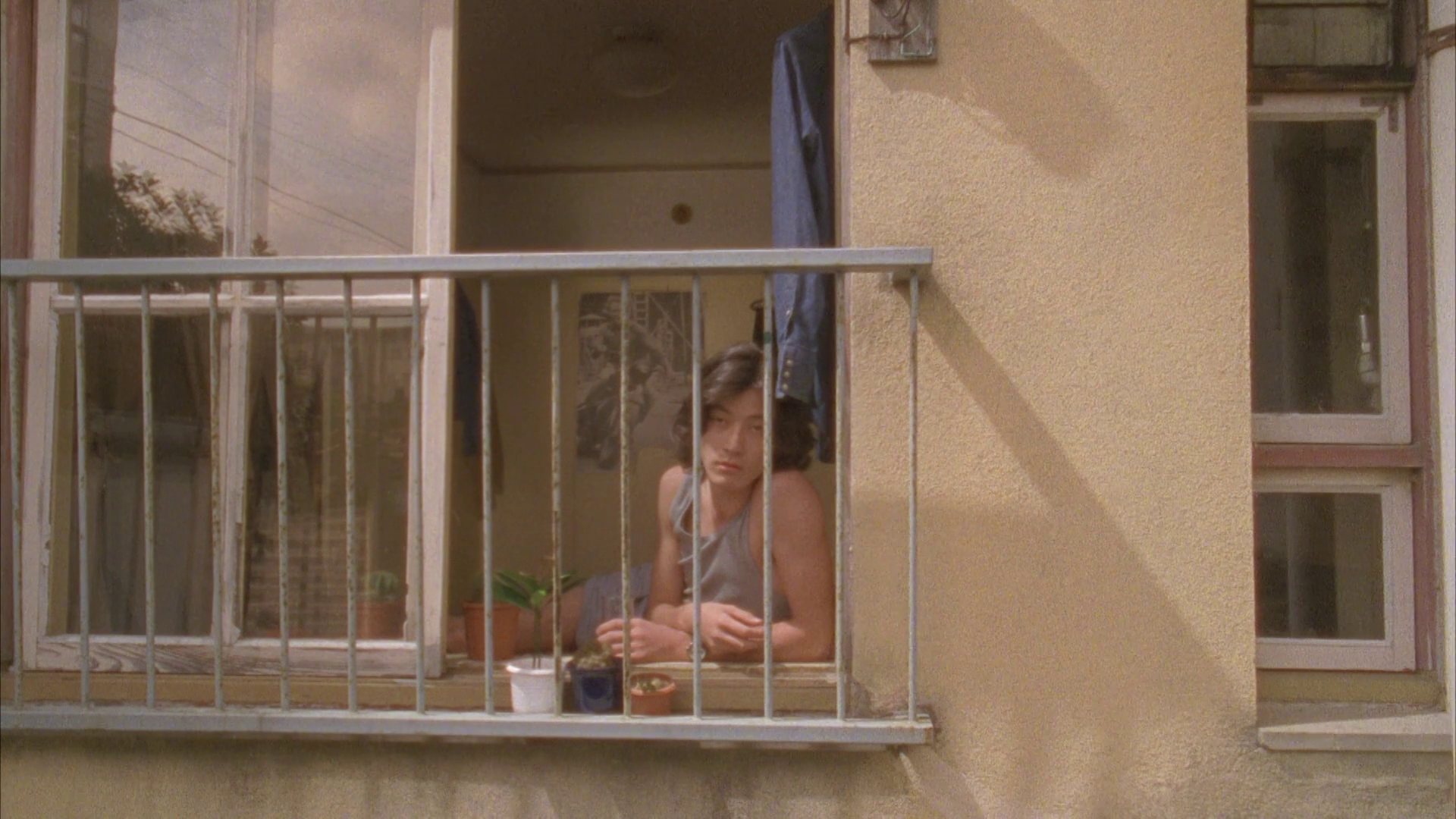
Beginning in conventionality, Shiota opens with the sweet and innocent friendship between kendo enthusiasts Takuya (Kenji Mizuhashi) and Satsuki (Tsugumi). Many seem to think they are a couple, but Takuya is quick to correct his friend telling him that they are merely “sparring partners” even going so far as to hand over a love letter, which he knows to be exactly the same as the letter his friend writes to all the other girls, on his behalf. As expected, Satsuki finds his behaviour insensitive, suspecting that Takuya himself has a crush on her but finally confessing her own feelings while he wheedles that he never said anything because of his sense of inadequacy explaining that just to be near her was always enough for him. Following this brief moment of connection, the couple embark on a “normal” teen romance, Satsuki taking the initiative with Takuya in bed with a cold to consummate their relationship. It does not go particularly well, in part because Takuya has a secret. He’s been secretly stalking Satsuki for ages, likes to break into her locker to smell her gym kit, and has a collection of keepsakes he’s stolen from her in addition to a series of illicit photographs and a tape of her using his family bathroom. The tape proves the last straw for Satsuki who then storms out calling him a freak and starts dating her handsome kendo club senior Uematsu (Kota Kusano) instead.
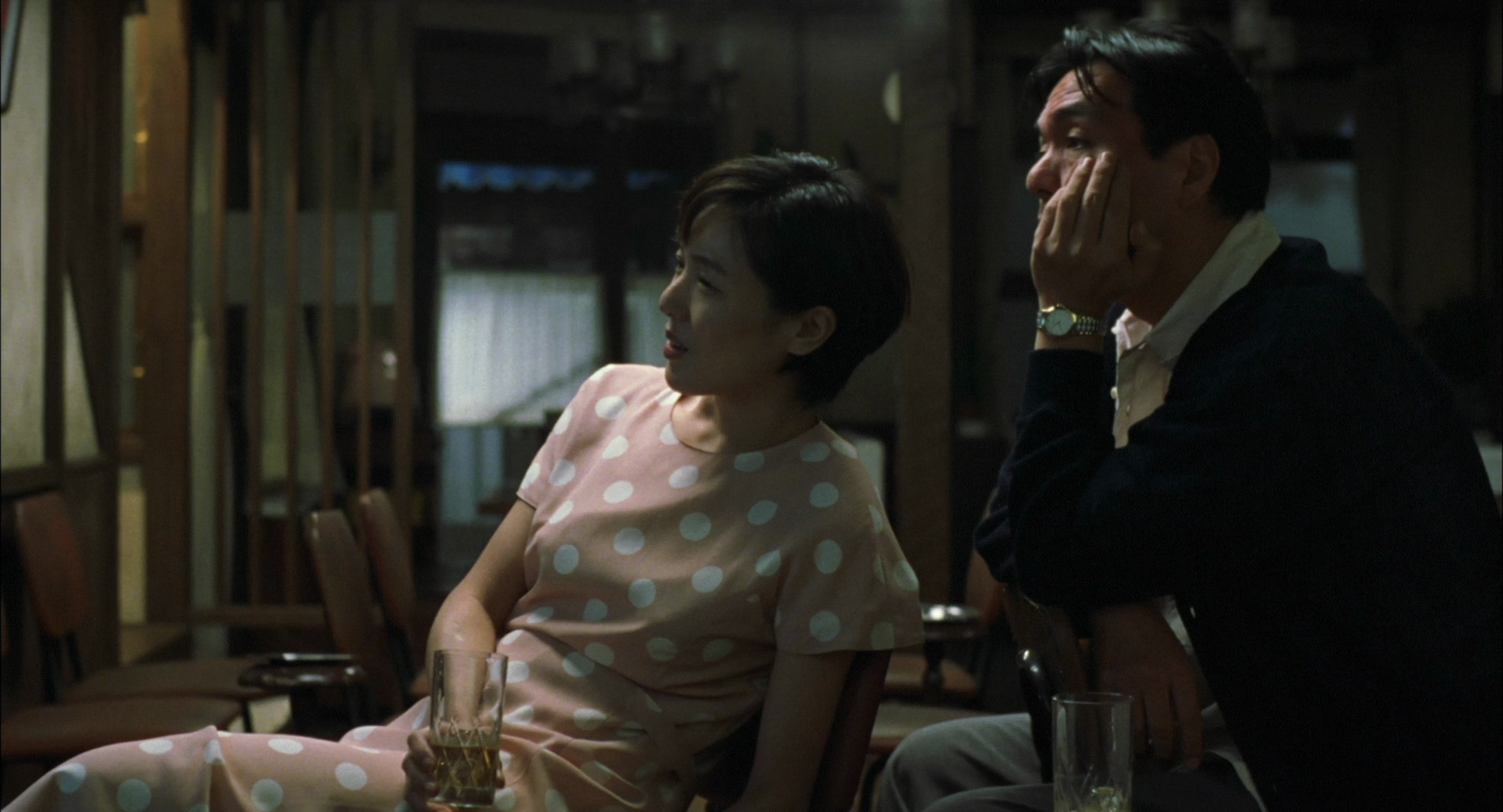
What Satsuki hasn’t figured out is that Takuya quite likes it when she’s mean to him, which is why he continues stalking her even after she starts dating the very “normal” Uematsu. Unexpectedly, she begins to discover that she quite likes, if not quite the process of hurting him, then watching him suffer which is why she makes him sit silently in a tiny cupboard while she has “normal” sex with Uematsu on a sofa directly opposite. The relationship between them is one of push and pull, Takuya initially embarrassed and ashamed of his masochistic desires explaining that “god made me wrong” while ironically driving Satsuki towards an awareness of her sadism. On the other hand, the relationship had always been unconventional in its reversal of gender roles, Satsuki quite literally leading while Takuya trails behind. She is the first to openly state her feelings and the first to initiate sex, while Takuya is somewhat feminised in his deference and timidity.
Nevertheless, Satsuki struggles to accept her capacity for sadism refusing to tell Uematsu why she broke up with Takuya but explaining that she wants a “normal” relationship in with someone with whom she would be able to discuss anything and everything honestly the irony being that she might have had that with Takuya but cannot with Uematsu because she is filled with internalised shame about the “perverted” pleasure she gains on witnessing Takuya wilfully degrade himself on her behalf. They are already in an accidental sado-masochistic relationship though they of course do not quite have the words to describe how they feel or what it is that exists between them. Their love inevitably heads to quite a dark place but even so leads to a kind of rebirth in which each fully accepts themselves for who they are along with their designated role within the relationship even if also knowing that others may not be quite so understanding.
For all of its provocative qualities, there is an underlying sweetness in Shiota’s unconventional romance even as he carefully inverts accepted genre norms the conventional indie background score perhaps ironically undercutting any sense that the relationship is actually as “perverse” as the teens sometimes feel it is even as they each struggle with their respective feelings and desires. Nevertheless he ends on a note of anxious ambivalence as the physically and emotionally wounded lovers remove themselves from mainstream society in order to embrace their authentic selves.
Original trailer (English subtitles)