Hibari Misora fights Edo-era corruption once again in another jidaigeki musical adventure from Tadashi Sawashima. Snake Princess (新蛇姫様 お島千太郎, Shin Hebihimesama Oshima Sentaro) sees her doing double duty as a sake-loving stage performer in love with a reluctant revenger, and an austere princess mourning the murder of her confidant and only friend but, as in some of her other films, the resemblance is never remarked upon nor is it any kind of plot point. There isn’t even really a “snake princess”, though snakes and the supernatural do play their part and there is perhaps less space for the derring-do and swashbuckling musical numbers which typically characterise a Hibari picture.
The film opens with stage performer Oshima (Hibari Misora) waking up from a drunken snooze on a riverbank and realising she’s been left behind by her acting troupe. Running into the mysterious Ittosai (Minoru Oki) on her way, she hurries on to the next town to catch them up while he heads in the opposite direction towards Karasuyama and the Princess Koto (also played by Hibari Misora). Meanwhile, in the town, a rowdy samurai starts a drunken fight in an inn, demanding to drink with the innkeeper’s pretty daughter Suga (Tomoko Ogawa). The innkeeper refuses, offering the excuse that his daughter is at the palace with the princess, but the samurai doesn’t take no for an answer and starts thrashing about with his sword eventually killing the innkeeper for the offence he feels has been caused to him. The innkeeper’s son Sentaro (Yoichi Hayashi), a former pupil of Ittosai, then kills the samurai in revenge and is forced on the run, taken in by the leader of Oshima’s acting troupe, Juzo (Takashi Shimura), who apparently knew his father well.
What ensues is of course a tale of intrigue and revenge mixed with mild romantic melodrama. Oshima begins to fall for Sentaro, but is warned that he is from a prominent non-samurai family and as such is unlikely to marry a travelling actress, itinerant players then belonging to a kind of underclass which is in part one reason why it is so easy for Sentaro to hide among them. Even so he is also subjugated by the samurai who frequently object to being ordered around by “commoners”, insistent on their privilege the refusal of which is the reason Sentaro’s father had to die.
Meanwhile, the Princess Koto is herself oppressed within the feudal system as a female ruling a clan in the absence of her father who has placed her in charge while he remains in the city. While Oshima falls for Sentaro, the relationship between Koto and Suga is perhaps transgressively equally close, Koto describing Suga as the only one she can trust within her own court and plaintively asking her to stay by her side forever. Unfortunately however Suga is murdered by the male court conspirators attempting to wrest power from the princess on her way back with evidence of their smuggling plot after meeting Ittosai on Koto’s behalf. Misled into thinking that Koto had his sister killed, Sentaro plots revenge but on learning the truth asks her why she hasn’t dealt with the wrongdoing among her own retainers, only later realising that even as the leader of the clan she lacks the power to do so and remains in a precarious position.
Arguably, Oshima has more freedom, fearlessly walking the roads alone, drinking and gambling with the men refusing to abide by traditional social codes though perhaps in some ways permitted to do so precisely because of her position within the entertainer underclass. A further gender reversal sees the fallen Sentaro temporarily resorting to sex work as a host at an inn drinking with a melancholy noblewoman who fully expects to bed him for her five Ryo only for Sentaro to become indignant and throw the money back in her face, much to Oshima’s approval though she later becomes jealous and irritated questioning him if he’s ever done this sort of work before as if it would actually change her feelings for him. While Sentaro is forced into but then rejects the subjugated female role, Oshima chooses the male solution of trying her luck at the gaming tables, occasionally charging into a fight wielding a nearby object such as a handy water bucket.
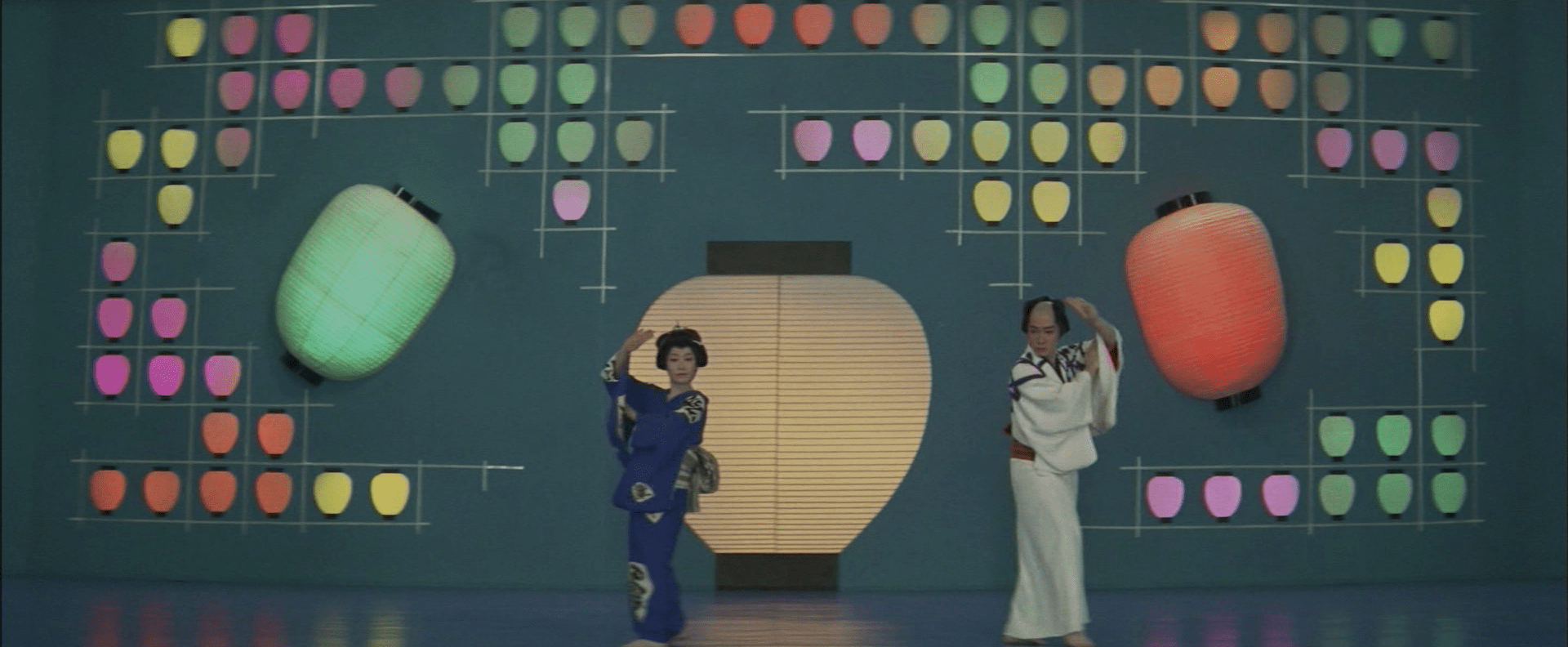
The snake theme of the title links back to the supernatural appearances of Suga’s silent ghost, protecting the princess with a wall of serpents when Sentaro plans to attack under the false assumption that she was responsible for his sister’s death. Musical numbers are largely restricted to a lengthy stage performance featuring Oshima and Sentaro’s evolving act utilising several sets and elaborate design while Sawashima ups the game a little from the lower tier Toei norm with varying locations shifting from a set-bound snowscape as Oshima is carted off by local goons, to a shot-on-location set piece as the conspirators take down a spy in the rocky desert. Revenge is eventually taken not only for the murders of Sentaro’s father and sister, but for the samurai transgressions of the Edo era, restoring order by wiping out the bad apples but also allowing Sentaro to free himself from his class-bound destiny and pursue a life, and love, of his choosing regardless of contemporary social codes.
Musical sequences (no subtitles)