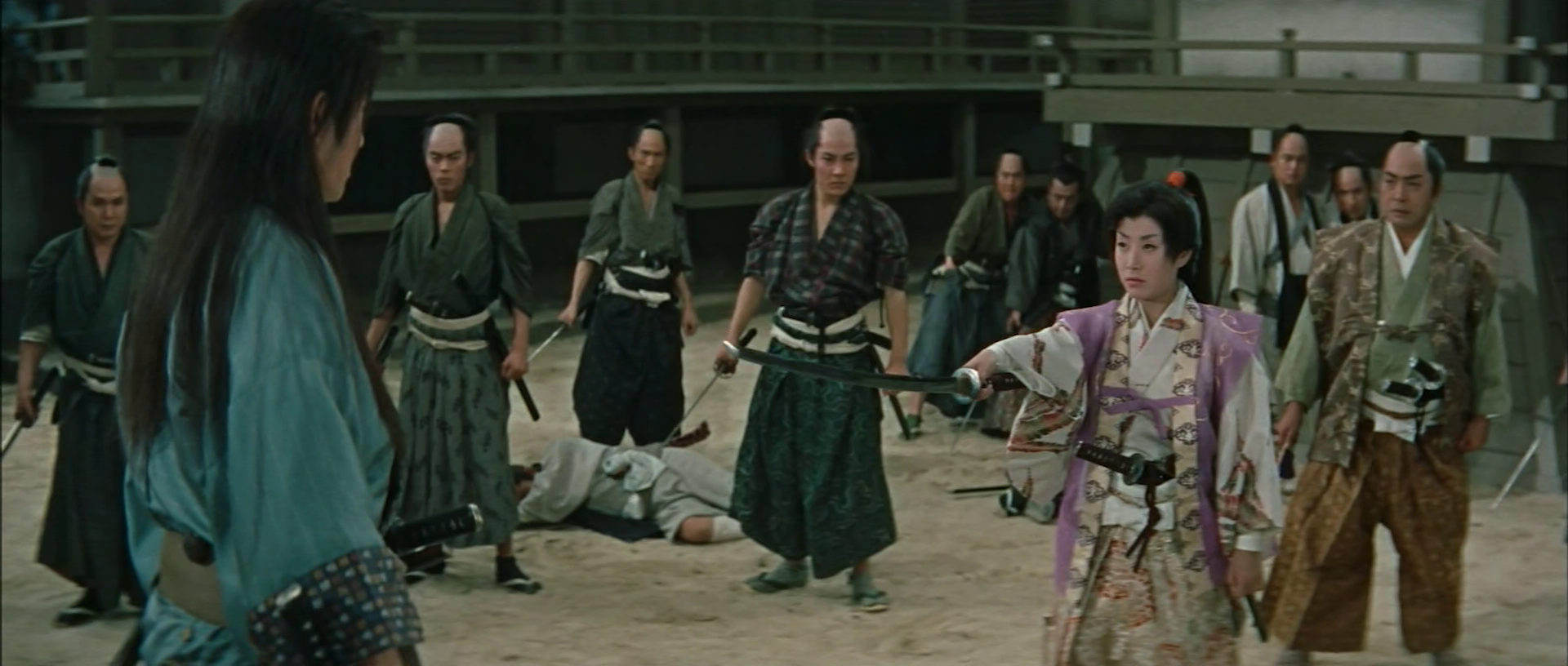
A wandering swordsman winds up in intrigue on returning to his fencing school to find his old master murdered in Yasushi Sasaki’s Sword of Destiny (孤剣は折れず 月影一刀流, Koken wa Arezu: Tsukage Ittoryu). A classic jidaigeki adventure, it nevertheless has to be said that this one is a little more sexist than most in actively pushing its series of female warriors into the background as the hero by turns sends them all back to typically feminine roles while declaring that he will be the one to claim vengeance and clear up corruption in the court itself caused by a woman’s apparent forgetting of her place.
At least, this is what Mikogami Genshiro (Koji Tsuruta) is told by an old friend, Izu, after an altercation with the fiery princess Kazu (Hibari Misora). The Shogun’s nurse, Lady Kasuga, has apparently taken an interest in politics and has most of the inner palace in her grasp enriching herself in the process. Izu believes that she may also be behind the assassination of Geshiro’s former mentor Ono while working in league with the Yagyu who coveted the position of fencing master to the Shogun. He asks Genshiro to kill her which he’s only too happy to do while seeking vengeance for Ono, but later gains a second reason after meeting the two orphaned daughters of a former retainer forced to take his own life thanks to Lady Kasuga’s machinations.
Itoya (Yoshiko Fujita) wanders round with a gun and disrupts Genshiro’s first assassination attempt. He later tells her to leave the killing business to him and live “the life of a woman” insisting that one girl has no power to kill Lady Kasuga anyway. Meanwhile, he also makes an enemy of the Shogun’s sister Princess Kazu after challenging her in the street on seeing her callous disregard for a peasant her horse had run over. Princess Kazu falls in love with him after he defeats her in a duel, temporarily rebelling in insisting she will resist a dynastic marriage and take no other husband though he eventually rejects her partly on the grounds of their class difference and partly because he is a wandering sword who lives in the moment and may know no tomorrow.
Nevertheless, she is later seen capitulating to her proper role as a princess who exists largely to continue the family line, marrying a man chosen by the Shogun and his advisors with no real power to chose anything other than her obedience. In much the same way he does with Itoya, Genshiro pushes her back towards the typically feminine while falling for Itoya’s meek, sickly sister Mine (Hiroko Sakuramachi) who is otherwise an idealised image of femininity in her softness and naivety while like every other woman in the picture falling for Genshiro because of his robust manliness and ability to protect her by gaining the sisters’ vengeance on their behalf.
Meanwhile, Genshiro also facing off against the rival Yagyu school whom he suspects of having killed Ono to usurp his place as the shogunate fencing master with the assistance of underling Takagaki who has now taken over leading to a mass exit of students fed up with his authoritarian teaching methods. Interestingly enough, Genshiro is temporarily imprisoned by the Yagyu alongside a dissident Christian whose death they’d faked while keeping him alive in order to torture the names of other Christians out of him. On fulfilling his request to take his cross to his daughter who has become a sex worker, Genshiro succeeds only in endangering her while she also falls in love with him.
All in all, he’s not much of a responsible hero also reckless with the life of his former burglar sidekick Kurobei (Shin Tokudaiji) who uses his ninja tricks to get him out of prison. As expected, it all ends with in a battle against a treacherous swordsman and the spineless Takagaki with the final revelation that Lady Kasuga (who just dies of old age) had not much to do with anything anyway despite having been a “meddling” old woman who forgot her proper place. Even Mine is forced to admit that she can’t come between Genshiro and his sword so she plans to become a nun while Kazu sends him an elaborate katana to remember her by certain that he will not accept a place in the Shogun’s household but will return to the road to continuing his training. In any case, a kind of justice is done and order restored even if that order is in itself fairly unideal.