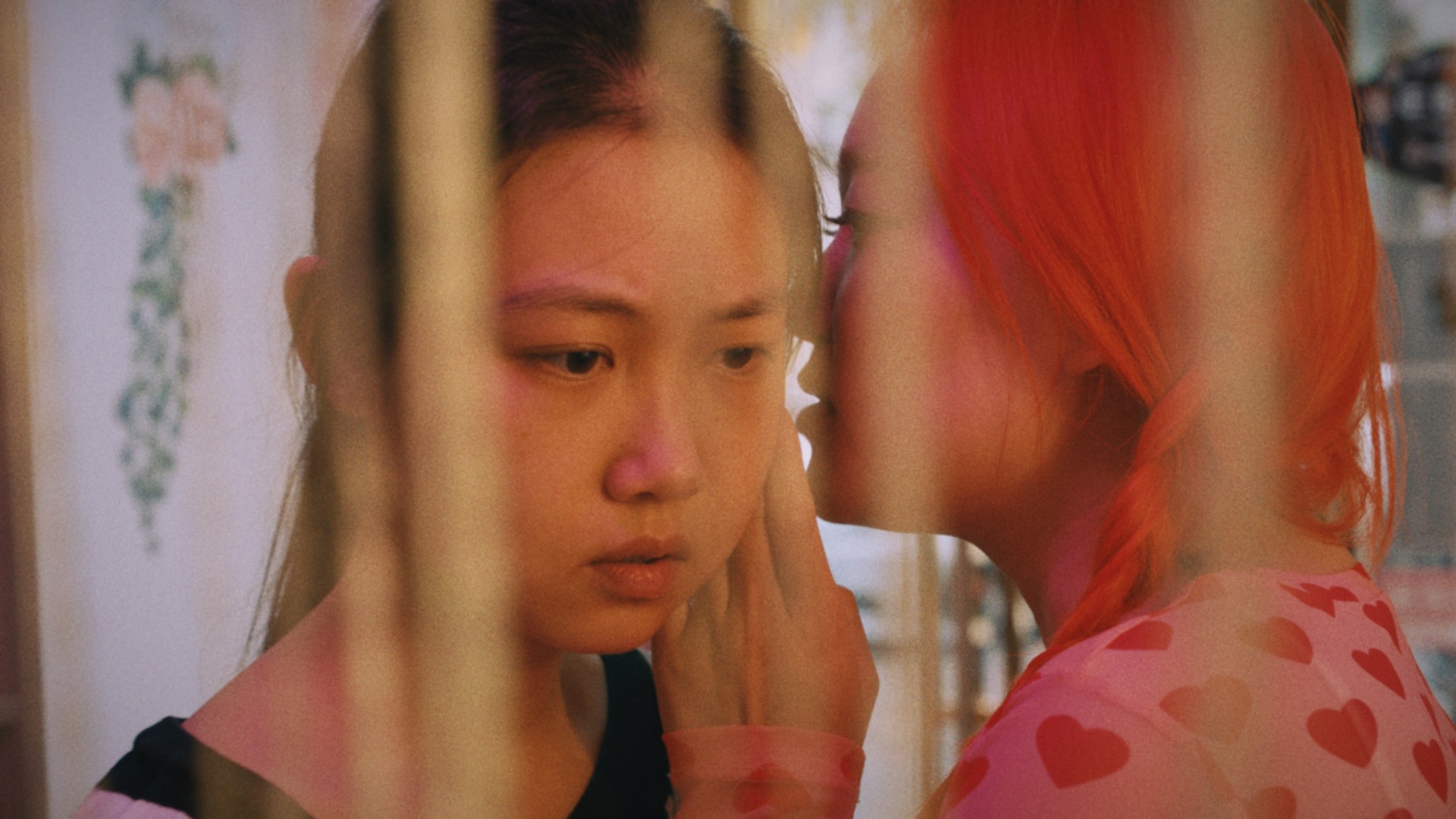Naoko, the heroine of Kenta Ikeda’s Strangers, says she’s been pretending all her life. She’s been pretending to be what everyone wanted her to without really knowing or thinking about what it was she wanted to be or who she really is. On a baseline level, Ikeda suggests that we are and remain strangers to ourselves while equally confused about those around us, seeing what we want or expect to see rather than who they really are.
In part that may explain why Naoko has stayed with her unfaithful fiancé Takeo who got a colleague pregnant and then seemingly abandoned her. Shimizu then began harassing Naoko, stalking her and making silent calls. To make matters worse, Takeo is often away on “business trips”. He’s not currently responding to her phone calls or messages and has just embarrassed her by not turning up to a family event. Naoko’s sister thinks she should leave him and doesn’t understand why she hasn’t already. But Naoko just sighs that she’s decided not to expect too much from life and seems prepared to put up with this degradation because she doesn’t think she deserves anything better.
That might be why she’s so drawn to her enigmatic colleague Yamaguchi who waltzes in past noon wearing a distinctive blue dress that floats in the air behind her. The other ladies at work gossip that their bullying boss Satome, who is married with two children, got her the job after picking her up on a dating app and the reason why she can get away with such unprofessional behaviour is because she’s sleeping with him. But Naoko later discovers that Yamaguchi’s dating app activities are a kind of side hustle in which she participates in idealised dating scenarios pretending to be the lover of lonely men who pay her handsomely for a few hours of fantasy romance.
Or as Yamaguchi describes it, the opportunity to experience only the good parts of love before you get sick of each other and run out of things to say. It sounds more than a little like the logic of someone who’s decided not to expect too much from life, and while it seems Yamaguchi may be trying to avoid her own grief and loneliness, it’s true that she otherwise remains a cypher. After losing contact with Yamaguchi and being left with her smartphone, Naoko receives a call from her handler who tells her that it doesn’t matter who she is or why she has “Yamaguchi’s” phone, all that matters is turning up at the appointment and never letting it slip that it’s all just role-play.
On her dating app profile, Yamaguchi’s face is blurred so that you only really see the image of her in her distinctive blue dress which Naoko too later starts wearing. The people around Naoko are often shot in soft focus so that we can’t really be sure of their identity beyond using their clothing to infer who they are. Men in particular are often shot from behind or with their faces out of frame as if they were all just a much of a muchness. We never even meet Takeo, who apparently does not return from his “business trip”. In any case, in agreeing to the fantasy date, Naoko is gradually taken over by the Yamaguchi persona. The spread of the graze she sustained at the beginning of the film seems to indicate the gradual erasure of her identity, yet in another sense becoming Yamaguchi also gives Naoko an excuse to stop pretending and accept herself or at least to start expecting more from life. She becomes more assertive, flirtatious, and confident in confronting Shimizu only to realise that she may not have been the mysterious force she felt watching her after all.
In her Yamaguchi persona, Shimizu describes Naoko as a like a colourless and doorless detergent, but she replies she’s been hiding all her life. She ran ran away from her problems, refused confronting Takeo or Shimizu, avoided being honest with her family and simply played up to the image they had of her of a shy and obedient woman. There might be something in the fact that Yamaguchi kisses her suggesting that Naoko may have been running away from her sexuality, but equally it could just be that this is how the Yamaguchi curse is passed from woman to woman. Having once assumed it, Naoko now must try to shake it off but that too might not be as easy as she might assume. Meanwhile, those around her also have their own secret lives and faces they keep hidden from others. Ikeda creates a atmosphere of eeriness and hovering violence amid the faceless city where it doesn’t matter who you are so long as you show up and everyone is to some extent participating in a temporary fantasy in order to overcome the disappointment of life in which as Naoko had told herself it seems better not to expect too much.