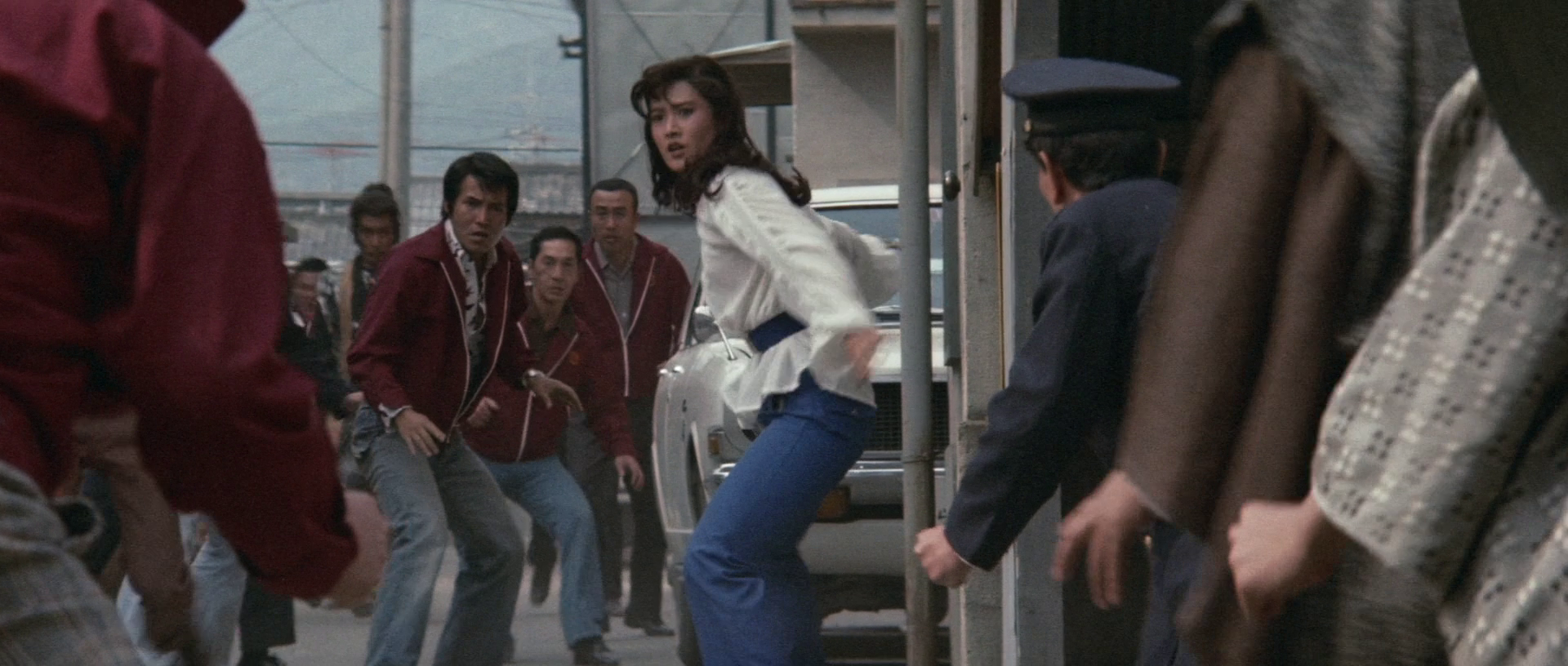
Though it’s tacked on to the Sister Street Fighter series, Level Five Fist (女必殺五段拳, Onna hissatsu godan ken) actually has nothing to do with it save borrowing a part of the title which is intended to signal the presence of its star. Thus, this is not really a martial arts movie but a much more conventional Toei action film in which the leading role is technically split between Etsuko Shihomi’s posh girl karate champ and Tsunehiko Watase’s sexist cop. It does however continue the smuggling theme with the drugs this time first being packed inside fish and then encased in Buddha statues to be exported to America.
Like many Toei films of the time, there is an underlying theme of anti-Americanism as the “Far East” big boss, posing as a Hollywood movie exec, is supposedly from there but has a strong accent suggesting otherwise. Meanwhile, the brother and sister at the film’s centre are a pair of children who were fathered by American servicemen at the bases in Okinawa who presumably took no responsibility for their upbringing. The brother’s father was black, while the sister’s was white, and though they have both suffered prejudice and discrimination because of their mixed ethnicity, it’s clear that Jim (Ken Wallace) has had it worse. Michi (Mitchi Love) makes good use of her native-level English abilities and martial arts skills to work as a bodyguard / interpreter for visiting dignitaries, but Jim seems to struggle to find employment and subsequently ends up working for a Korean gang run out of a local nightclub.
The pair have a dream of saving up enough money to return to Okinawa, which was returned to Japan in 1971 after an extended period of US occupation, and opening a restaurant which the film positions as a desire to escape from the racism they experience on the mainland. When Jim says that Kiku (Etsuko Shihomi) is their only friend, he half implies that the discrimination they face is down to being Okinawan rather than their mixed ethnicity which would continue to be an issue even on the islands as it was in their childhood even if there may be more understanding given the continuing presence of the American military and larger numbers of mixed-ethnicity people. In any case, it’s true enough that even those from Okinawa do also experience discrimination on the mainland and are not always accepted as “Japanese” while their Okinawan identity is not respected either.
Kiku is trying to protect her friends, but finds herself hamstrung by rigid cop Takagi (Tsunehiko Watase) who also happens to be the son of a friend of her father’s. Kiku’s father is apparently a self-made man and successful kimono merchant married to a more conservative woman with higher social ambitions. As the film opens, Kiku is dressed in a kimono and being subject to a formal omiai meeting for an arranged marriage with an admittedly promising candidate who graduated from an elite university and works for a prominent bank. But Kiku looks bored throughout and defiantly flouts social convention by suddenly claiming to have an appointment and walking out, much to her mother’s embarrassment. Her father lets her go and is apparently less bothered about this sort of propriety though later trying to put his foot down when she leaves the house dressed like a hippy rather than in a fine kimono which is not, after all, a very good advert for the family business.
Her father also tries to set Kiku up with Takagi, but like her mother, Takagi also tells her to keep her nose out of the case and “try trusting a man for once”. He criticises her for saying that she doesn’t want to lose to a man and explains that men are attracted to women because of their “gentleness.” He adds that cooking and raising children are what make women happy, with the clear implication that Kiku is in the wrong for flouting conventional gender roles and should quickly conform by getting married and becoming a wife. Kiku appears to give him the benefit of the doubt and this confusion over gender roles is compounded when she poses as a boy and takes a job as a extra on the jidaigeki film set at the studio which turns out to be a front for drug runners. A queer-coded actor who is later told off for “stalking people again” tries to hit on her in a clear allusion to her masculinity. But unlike in the Sister Street Fighter films, she is ultimately defeated and tied to a log with a buzz saw coming at her only to be saved by the intervention of Takagi while the final scenes see her supporting him after he is (possibly fatally) injured defeating the bad guys.
All in all, it’s some rather confusing messaging but seems to come out on the side of male authority as represented by the police rather than Kiku’s father who is depicted as a weakened figure of masculinity owing to being henpecked by his wife and hoodwinked by his feisty daughter. Even the grinning sap from the gym who tried to put Chanel No. 5 on Kiku’s karate outfit, much to her annoyance, is later revealed to be an undercover cop. Which is all to say, that Kiku’s martial arts ability is almost a kind of joke and something that places her outside of conventional gender norms which should otherwise be “corrected” rather than praised, as it was in the Sister Streetfighter series which placed more emphasis on martial arts philosophy. Then again, the original trilogy ended on a similarly sour note in reaffirming Koyu’s maternity. It seems it’s less sisters doing it for themselves, than sisters doing as they’re told, which aside from anything else is a disappointing conclusion to one of the few female–led action franchises of the 1970s.
Original trailer (English subtitles)