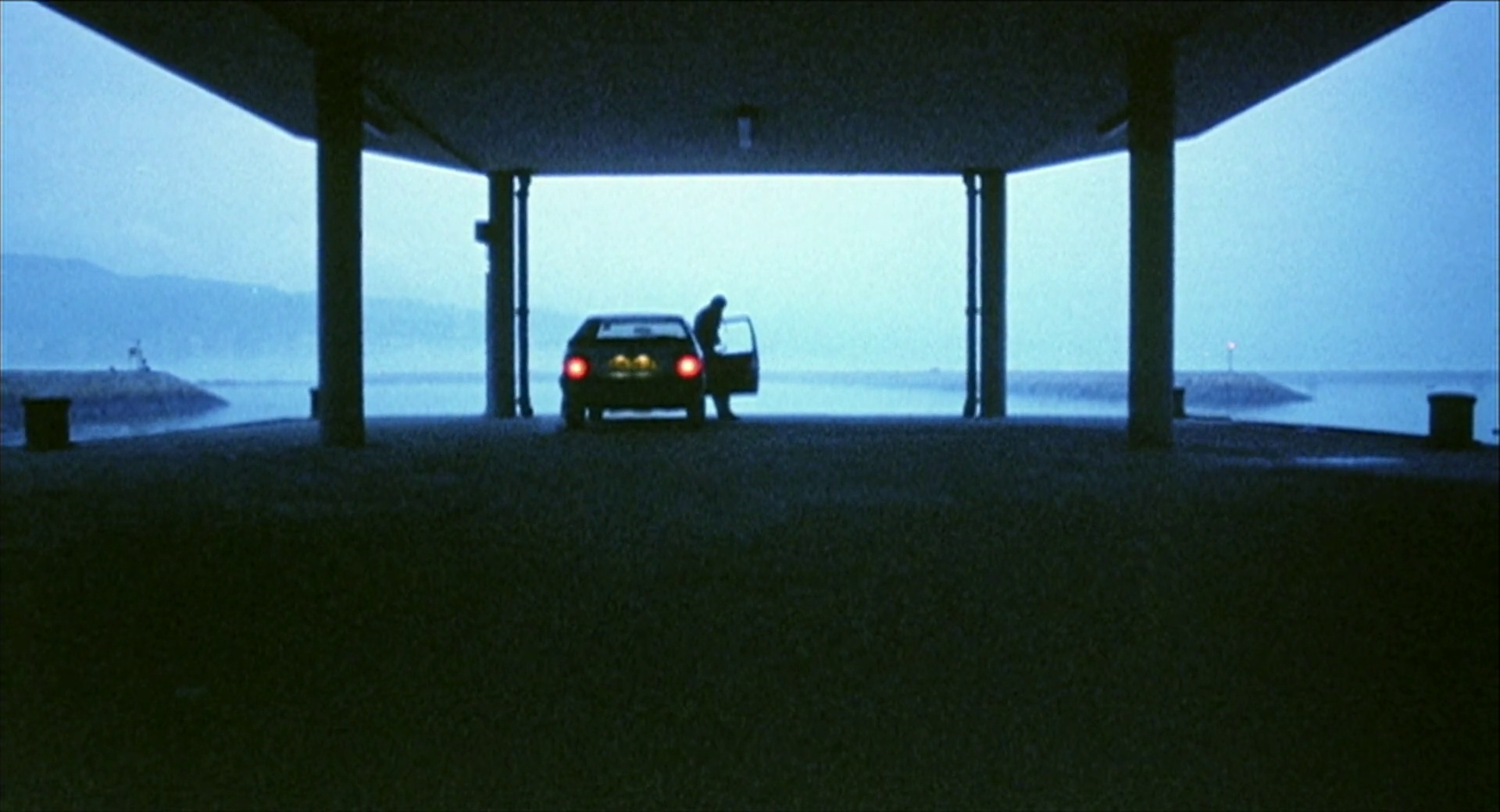
“We’re outmoded characters,” a dying man laments, having previously advanced that “nostalgia is one of our saving graces.” The heroes of The Killer (喋血雙雄) are indeed remnants of an earlier time, out of place amid the modern city and adhering to a code that has long since fallen by the wayside. “Our world is changing so fast,” hitman Jeff (Chow Yun-fat) exclaims of a Hong Kong hurtling not only towards the Handover but an increasingly amoral capitalism in which friendship and brotherhood no longer have any currency.
We can tell this straightaway from the fact that the man who ordered the hit on the drug lord Jeff took out at the dragon boat races was his own nephew, Weng (Shing Fui-on). To tie up loose ends, Weng also sends his own hitmen to take out Jeff, who can’t be sure if his handler and best friend Sidney (Chu Kong) is involved in the plot to knock him off. Later in the film, Inspector Li (Danny Lee) asks what Jeff will do if Sidney betrays him, but he merely says that he will still treat him as a friend because he has been good to him in the past. Jeff says this in an abandoned church, echoing not only the codes of jianghu brotherhood now largely absent in the contemporary society but Christianising notions of forgiveness and acceptance.
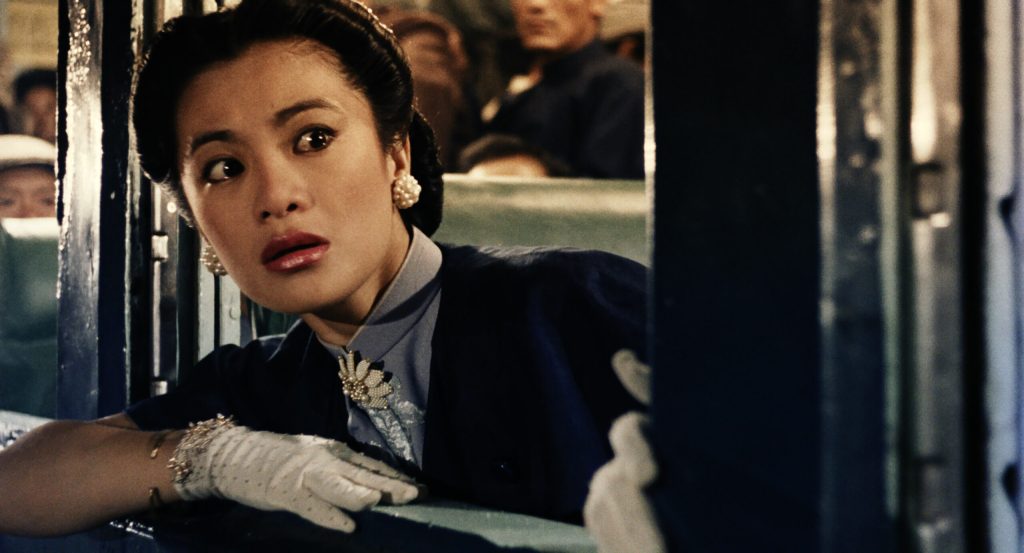
Jeff claims that he isn’t a religious man but appreciates the tranquillity of the disused chapel. Inspector Li meanwhile is often pictured next a statue of the Buddhist god of war and dressed in black in opposition to Jeff’s white, but what emerges is that the two men are effectively the same and somewhat interchangeable. Jennie (Sally Yeh), the nightclub singer Jeff accidentally blinded during a a chaotic hit and subsequently falls in love with, first mistakes Li for Jeff while Woo also pictures him sitting in Jeff’s chair and pulling a gun on his partner in much the same way Jeff cooly dispatched an assassin sent by Weng. Chang had told Li that he looked exactly like what he was, an undercover policeman, which is obviously a problem, but Jeff remarks that he is a “very unusual cop,”while Li agrees he’s a very unusual killer.
In some senses, Li will also become the killer of the film’s title in the closing moments, a man who believes in justice but is not himself believed and knows that there will be no real justice for a man like Weng. Both men share a code which is essentially the same, a more primal kind of morality largely incompatible with the modern society and in many ways rightly so. Li even says that Jeff does not look like a killer, that there’s something “heroic” about him, and that his eyes are full of passion as if he had a dream. His words have a kind of irony to them, but Jeff does indeed have a dream in the desire to gain redemption for himself by restoring Jennie’s eyesight, which is the reason for his last big job having now been reformed by her no longer believing that the people he killed deserved to die but that everyone has a right to live.
Despite the triangular relationship with Jennie, there is an undeniably homoerotic tension in the connection between Li and Jeff even if they are also two sides of the same coin. They train their guns on each other and lock eyes, but unexpectedly find a kindred spirit in a man who should be an enemy. “The only person who really knows me turns out to be a cop,” Jeff chuckles but has an equally deep relationship with handler Sidney just as Li has with parter Chang (Kenneth Tsang) while the homosociality that defines their world is subverted by Weng who simply shoots his own underling when he becomes inconvenient to him.
Both Li and Jeff are effectively men left with “no way out” and “nowhere to go” because their code of brotherhood is no longer understood by the contemporary society. Jennie’s progressive loss of sight also echoes their dwindling futures as if the light were going out of their world long before Woo shatters the statue of the Virgin Mary and unleashes the doves of futility inside the no longer quite so tranquil church that becomes the final resting place of manly honour and brotherly love. “Perhaps we are too nostalgic,” Jeff sighs but nostalgia is indeed his saving grace in a world in which honour and friendship exist only in a mythologised past or may never have really existed at all.
Trailer (no subtitles)