“I see hope! Let’s change direction” a distressed woman shouts in a park, “We should follow the wind, let’s hold hands that way you won’t get lost.” Her interjection is perhaps unexpected, in its own way sad, but also a sign offered to the melancholy protagonist of Kim Jong-kwan’s Shades of the Heart (아무도 없는 곳, Amoodo Eobneun Got), a man who has become without quite realising it “someone who waits” yet through encounters serendipitous and otherwise begins to see new paths in front of him, turning a corner into another story.
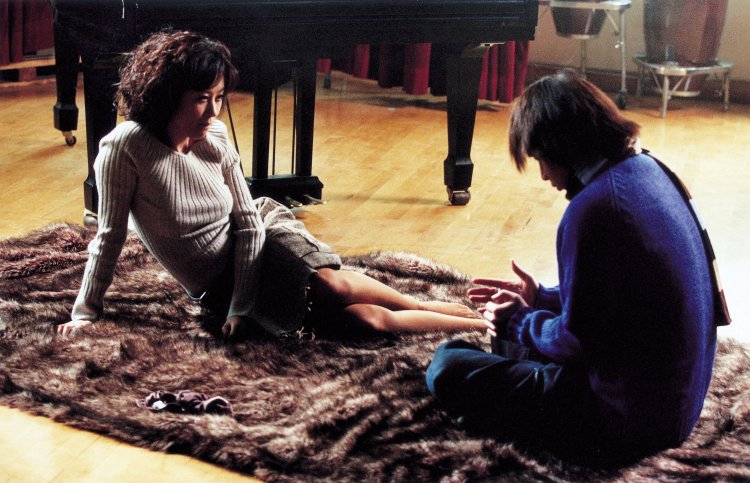
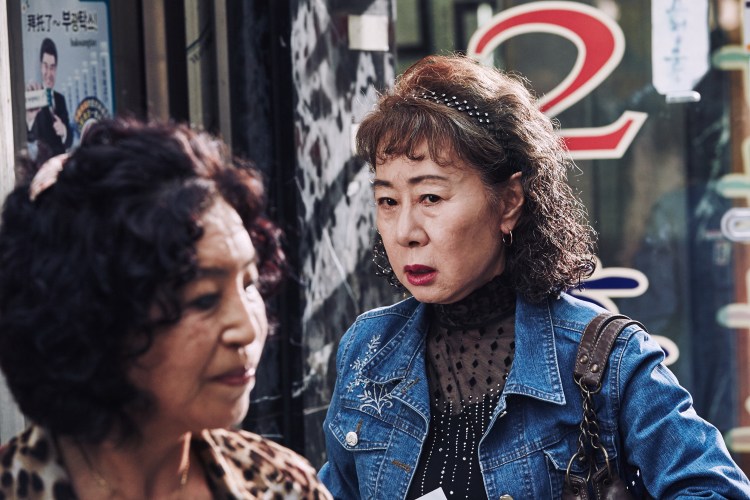
Novelist Chang-seok (Yeon Woo-Jin) has just returned to Seoul after seven years abroad following the breakdown of his marriage in the UK. He has begun to have strange dreams, seeing an older version of himself and presumably his wife walk away from him and eventually disappear. Yet each of the people he meets is also in someway burdened by a sense of loss or despair, his first meeting with his mother who appears to have some kind of dementia and does not initially recognise him thinking once again she’s on her first date with his father. Her sadness is the loss of past and present but also of future, telling her son on finally recognising him not to smoke so much so he won’t die young like his dad.
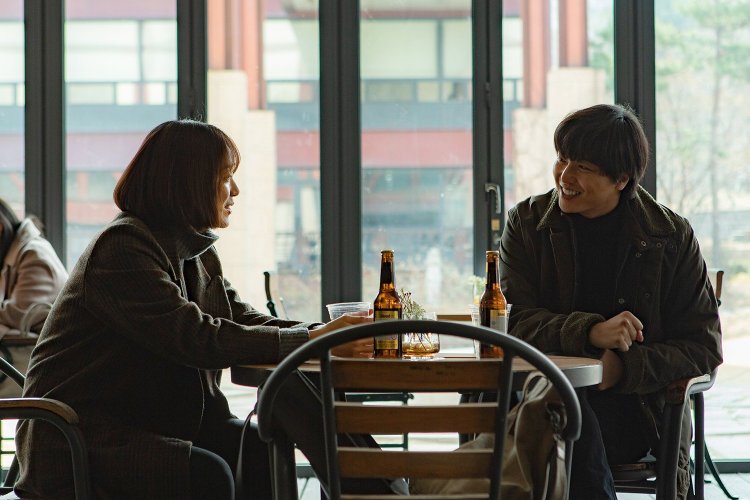
Chang-seok had apparently given up smoking, but is motivated to start again perhaps seeing little point in extending his life, accepting some unusual Indonesian cigarettes from a former colleague now his editor who eventually tells him of her failed love affair with a young exchange student which apparently ended partly because he could not acclimatise himself to the harsh winters of Seoul. The other reason perhaps echoes something in Chang-seok’s own life though also tinged with a different sense of sadness. A serendipitous meeting with a former acquaintance meanwhile takes a turn for the strange, photographer Sung-ha (Kim Sang-Ho) somewhat manic in his ecstasy in having run into Chang-seok explaining that his wife is terminally ill yet a Buddhist monk had told him he’d run into someone he knew who would bring him luck. On the other hand, Sung-ha also shows him a vial of cyanide he’s managed to procure apparently planning to use it to take his own life after his wife dies but now filled with an almost certainly false hope in the strange power of religious mysticism. “I don’t believe in all that, but people.. they need to hang their hope on something” he explains.
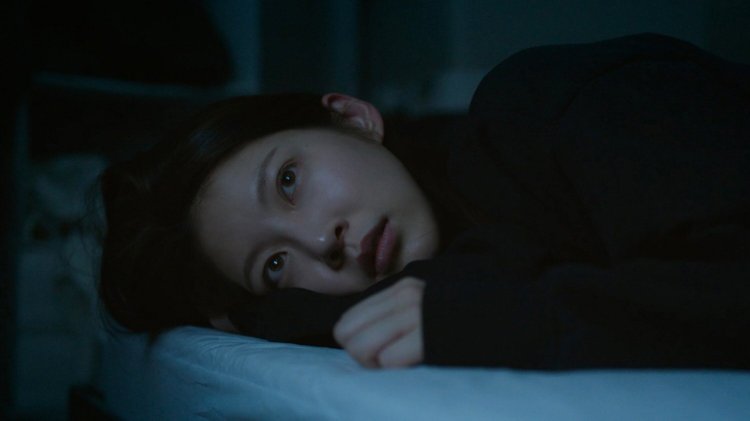
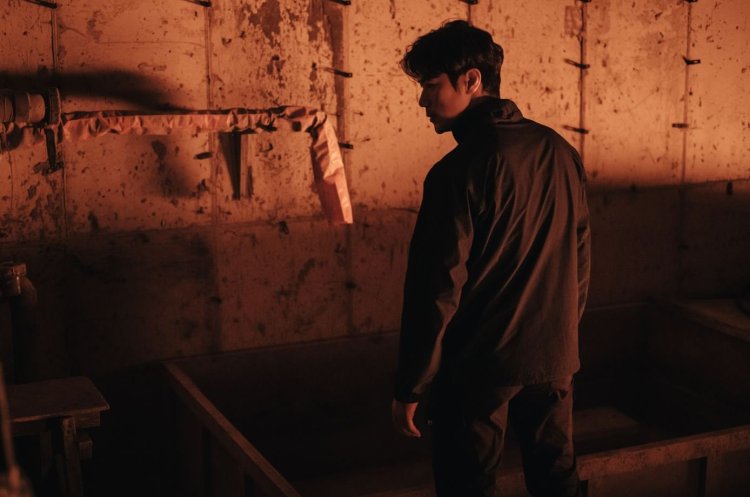
Chang-seok may not have much of a sense of hope, but what little he has he’s hung on people or on art. He is forever “waiting” for someone who may or may not arrive or even exist, making notes in his notebook or wandering around the surprisingly lonely streets of Seoul after dark pausing by the now obsolete phone booths filled with the detritus of city life unsure whether or not to make a call. His final conversation is with a woman who tells him that she has no memories of her own, having been robbed of her past, and more, in an accident and now “buys” them off her customers swapping free drinks for personal stories while writing poems about their lives. “No one is coming, but he became someone who waits” she writes of Chang-seok, their meeting oddly mirroring his first in its mixture of fiction and reality along with relationships forged through the exchange of stories true or otherwise. As he’d said, sometimes a made up story can be the more truthful.
“But they come in the depth of despair, miracles” Sung-ha had added hopefully seconds after saying he didn’t believe in them, each of Chang-seok’s encounters a tiny miracle in itself. Imbued with a deep sense of melancholy and loneliness, Kim’s delicately scripted ethereal drama is an exercise in grief and despair Chang-seok’s sense of fiction and reality beginning to blur even as he begins to find the urge to write again and with it perhaps to live again too. “I see hope!” the woman shouts once more, restored something as she takes her place in a new story, Chang-seok turning the corner and beginning once again to dream.
Shades of the Heart screens 14th November as part of this year’s London Korean Film Festival.
Original trailer (English subtitles)