Who doesn’t love a festival? The hero of Norifumi Suzuki’s Festival Champ (お祭り野郎 魚河岸の兄弟分, Omatsuri yaro: Uogashi no Kyodai-bun) loves them so much that he travels all over Japan to help out in places where young men have become thin on the ground thanks to increasing urbanisation and rural depopulation. Following the success of Suzuki’s entries in the Truck Yaro series in 1975 and 1976, the film was part of a new line of comedies and sports movies launched by Toei as well as a vehicle for Hiroki Matsukata who was trying to move on from yakuza movies.
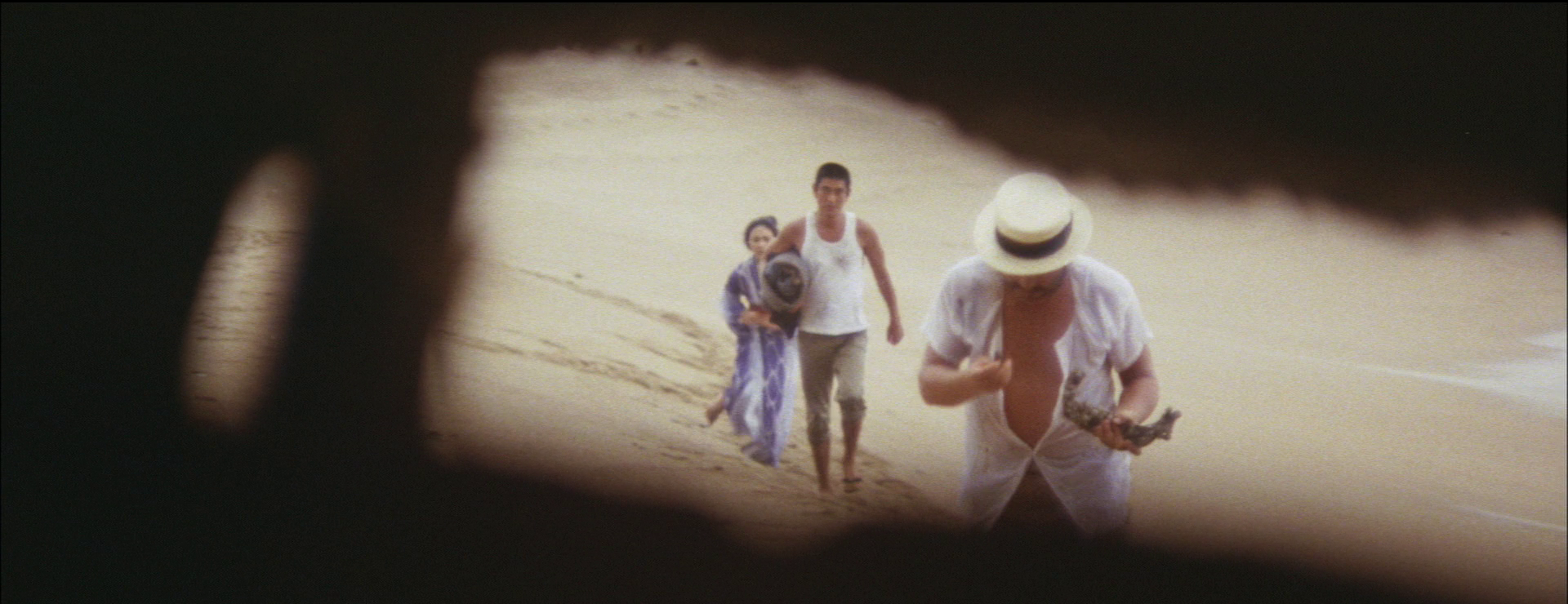
Katsuo (Hiroki Matsukata) is however something of a goodhearted bruiser who is always getting into manly scraps and especially at the festivals he travels to which is a pretty good hook for an ongoing series. But it’s not all that great for his employer who runs a family fishmonger’s at the Uogashi fish market and complains that Katsuo’s always running off and causing trouble. The fish market itself takes on an exoticised quality in the opening sequence which features a voice over from karate queen Etsuko Shihomi, here in a purely dramatic role, who is the daughter of a well-to-do traditional Japanese restaurant and travels there daily by speedboat to pick up the best fresh fish available. Suzuki throws in some documentary-style stock footage and statistics about the market that lend a strangely corporate feel, but then homes in on its capacity as a community hub. Kiyoko says it’s her favourite place precisely because there’s nothing formal about it. Deals are done through body language and you don’t need any kind of resume to work there, everyone’s welcome.
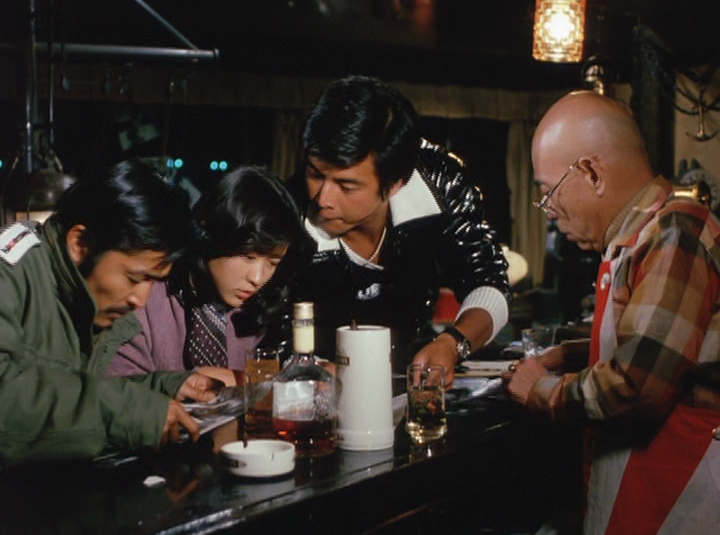
That may be the implied contrast between Kiyoko’s father, who owns an upscale place and cultivates genuine relationships with local fishermen and brokers, and local boy made good Kurosaki who has supposedly become the CEO of a restaurant chain, itself a symbol of the soulless corporation of ‘70s Japan. Kurosaki rocks up dressed like a yakuza, but everyone treats him as a successful businessman and in part thanks to Katsuo’s boss Zenjiro’s recommendation is eager to make deals with him but predictably he’s running a huge scam that could destroy the local economy. Zenjiro is later faced with the difficult decision of selling his family business to repay all the other fishermen and brokers that have fallen foul of him.
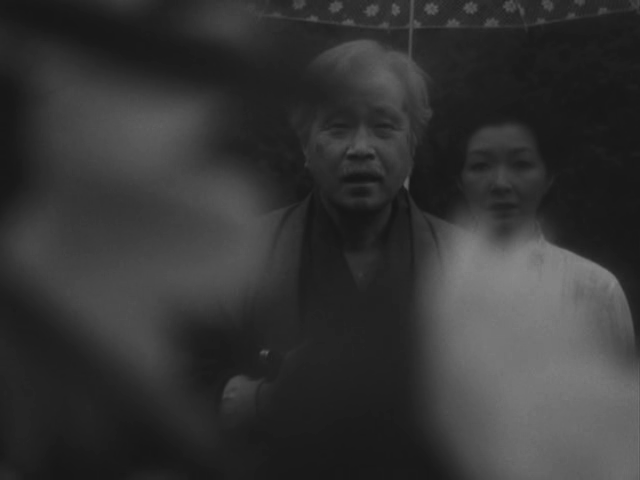
It’s this societal sense of unfairness that stripper Kumi (Terumi Azuma) hints at when she says she feels “frustrated” and that her long-lost brother Eiji (Toru Emori) probably feels even more frustrated than she does after he slaps her having found out that she’s become a burlesque dancer. As she points out to him, he ran away from home and left her behind with the aunt that was cruel to them so what exactly he expected her to do is a mystery. In the end, it’s his own fault for abandoning her, so he has no leg to stand on in criticising her for the way she’s lived her life. Kumi is well accepted in the local community and walks around in very elegant attire which gives her the air of an “ojosan” or upperclass lady to much greater extent that Kiyoko has in her love of the earthy world of the fish market. The fact that she turns out to be suffering from a tragic terminal illness perhaps only reinforces this sense of unfairness, that the modern world has essentially poisoned her and she can no longer survive in it.
The only things that give her solace are Katsuo and the idea of joining in carrying a shrine festival which would seem to be ways of reconnecting with a more essential Japaneseness. Despite his rowdiness, Katsuo is as she describes him the kindest person she’s ever met and a more positive vision of a still traditional masculinity that looks to protect the community and those around him. He gets into a fight with Eiji, but after exchanging a few blows the men become firm friends, while it’s trying to hook his wimpy friend Kinichi up with a date that brings him to Kumi in the first place. Meanwhile, it seems like Ayuko (Junko Natsu) has a crush on him and despite Zenjiro’s exasperation with Katsuo, everyone expects that he will eventually marry her and take over the family business.
And so, it’s only a violent, but also quite funny, intervention from Katsuo that can eventually overcome the disruption Kurosaki threatens. Suzuki throws in a lot of his trademark weirdness including all of Zenjiro’s other daughters having fishy names, and a local sex worker who is insatiably aroused by octopuses followed by a gag in which Katsuo is trolled with a suggestive-looking shellfish, but mostly rests on a sense of qualified wholesomeness and community all carried on Katsuo’s broad shoulders as the lone guardian of a more essential Japaneseness otherwise uncorrupted by venal post-war capitalism.
*Norifumi Suzuki’s name is actually “Noribumi” but he has become known as “Norifumi” to English-speaking audiences.


















