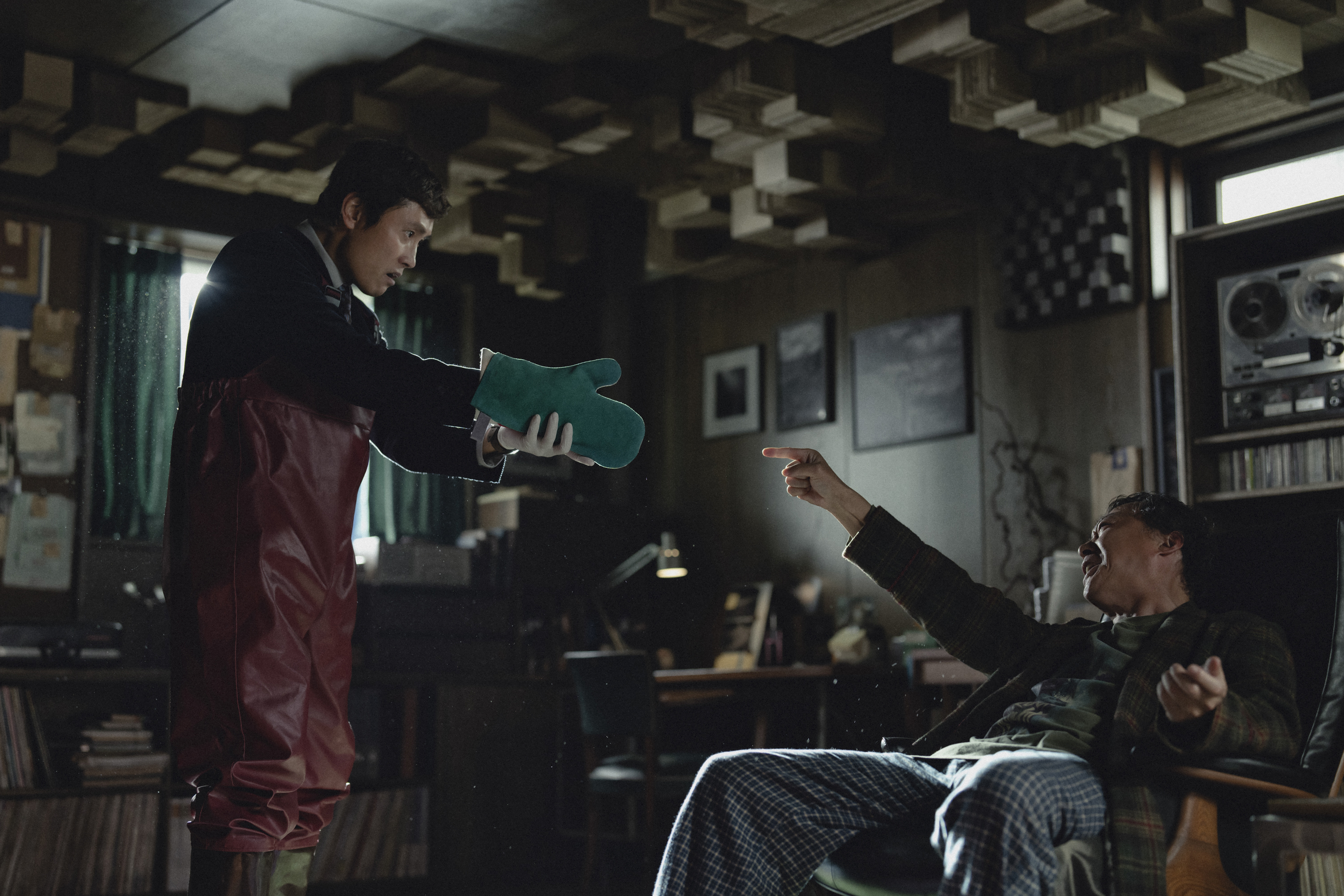
Most of the time, when someone says they had no choice, they’re paradoxically admitting that they had one, but they expect to understand the choice they’ve made because we would have done the same or can’t reasonably expect them to accept the consequences of the alternative. “No other choice,” on the other hand, is self-contradictory, clearly stating that a choice does indeed exist. Perhaps that’s why it seems so irritatingly disingenuous every time it’s said to Man-su (Lee Byung-hun), even if he eventually succumbs to its self-absolving qualities.
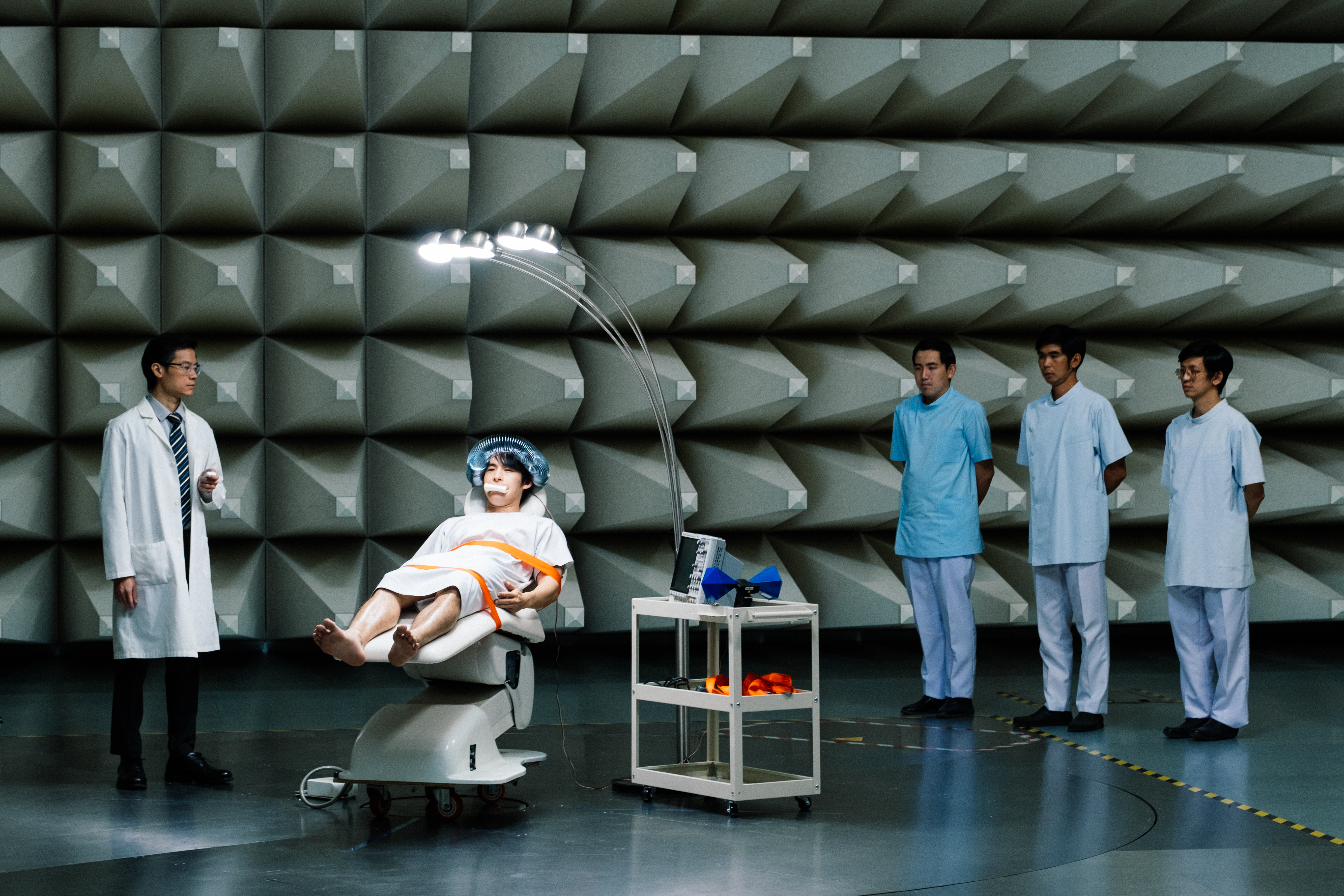
In any case, it’s this sense of powerlessness that’s at the centre of Park Chan-wook’s satirical drama as a middle-aged man finds himself suddenly exiled from the upper-middle-class lifestyle he’s worked so hard to build for himself when his company’s taken over by an American firm who have “no other choice” than to shed some staff. Man-su is blindsided by this corporate betrayal, attending self-help sessions that remind him there’s no such thing as jobs for life any more. Losing his job wasn’t his choice, but in some ways perhaps that makes it worse.
What connects him with the other men in his position is that he’s obsessed with getting another job in the paper industry rather than exploring other options. All of these men are fixated on getting back what they feel has been taken from them. Not only is Man-su dead set on getting another job in paper, but on holding on to the family home from which he was displaced as a child and has only just managed to reclaim. To that extent, what he wants is a return to a past that doesn’t quite exist any more or exists only in his memory and is therefore unattainable.
Losing his job also leaves him displaced within his family as his sudden inability to keep them in the manner to which they’ve become accustomed eats away at his sense of masculinity. They’ve already had to exile the dogs, leaving his young daughter distraught, while his wife, Miri (Son Ye-jin), has started working again, further emphasising his failure as a provider. Witnessing one of the other men’s wives cheating on him with a much younger lover, Man-su too begins to fear that his wife no longer sees him as a man and will cheat on him too with someone who better fulfils the codes of masculinity. Yet it’s his stubborn male pride that undermines his positions much more than the unfortunate fact of having lost his job, which wasn’t after all something he had much control over. The wives are all much more pragmatic and come up with realistic solutions such as ruthless belt tightening and ceding a little ground by voluntarily giving up anything inessentials while encouraging their husbands to be a little more pragmatic and consider new directions rather stubbornly fixating on reclaiming the life they had before.
That might be Miri decides to just sort of go with it even after beginning to suspect that Man-su has something to do with the disappearance of his rivals. At least he’s being proactive, even if it’s not really the best way to go about it, and by burying a few bodies there, he’s basically made it impossible to sell the house which is one goal achieved. It’s not losing your job that’s the problem, it’s how you deal with it, one of the other men’s wives insists as even Man-su ironically berates him for not listening to any of his wife’s “sensible” suggestions. Then again, the fact Man-su is eventually offered a job training AI replace him invites the suggestion that he’s basically killing all the other workers in the hope of clinging on to the wheel as soon as possible. The managers state they had “no other choice” about that too, and are grinning with the blinkered vision that prevents them from realising there’ll be no need for managers when there’s no one manage.
In any case, the fact that Man-su walks around for with toothache for a significant amount of time echoes the hero of Aimless Bullet and suggests that perhaps things aren’t all that much different in the Korea of today caught between deepening wealth inequality, exploitative working conditions, and employment precarity presented by the rise of AI and increasingly globalisation. There is something quite sad about the devaluing of these skills in that what Man-su and the other men share is reverence for paper, the beauty and texture of it, along with the craftsmanship and pride in their work that now seems to belong to a bygone era. It seems that the dog-eat-dog world of capitalism leaves Man-su with “no other choice” than to do what he did and leave others with no other choice but him, but all he’s really done is seal his own fate in a futile attempt to hold on to a past that is rapidly slipping away.
No Other Choice screens as part of this year’s BFI London Film Festival.
Trailer (English subtitles)