 Female suffering in an oppressive society had always been at the forefront of Mizoguchi’s filmmaking even if he, like many of his contemporaries, found his aims frustrated by the increasingly censorious militarist regime. In some senses, the early days of occupation may not have been much better as one form of propaganda was essentially substituted for another if one that most would find more palatable. The first of his “women’s liberation trilogy”, Victory of Women (女性の勝利, Josei no Shori) was released in 1946 and expressly embraced the democratic philosophy espoused by the American authorities which necessarily included a motion towards female emancipation.
Female suffering in an oppressive society had always been at the forefront of Mizoguchi’s filmmaking even if he, like many of his contemporaries, found his aims frustrated by the increasingly censorious militarist regime. In some senses, the early days of occupation may not have been much better as one form of propaganda was essentially substituted for another if one that most would find more palatable. The first of his “women’s liberation trilogy”, Victory of Women (女性の勝利, Josei no Shori) was released in 1946 and expressly embraced the democratic philosophy espoused by the American authorities which necessarily included a motion towards female emancipation.
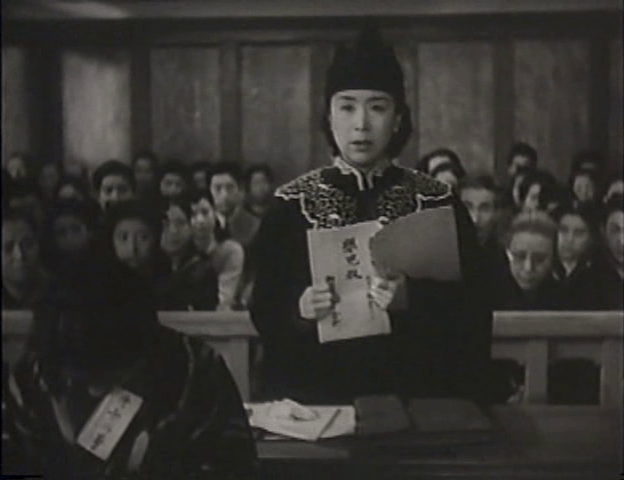
Played by Mizoguchi’s muse Kinuyo Tanaka, our heroine is Hiroko – a young woman working as a lawyer defending women against the cold and hard face of the law. Her family situation is, however, complicated. Her father having passed away, Hiroko’s sister Michiko (Michiko Kuwano who sadly passed away during shooting after collapsing on set) married the prosecutor Kono (Kappei Matsumoto) who financially supported Hiroko so that she might become the lawyer she is today. Meanwhile, Kono is also responsible for the arrest and incarceration of Hiroko’s fiancé Yamaoka (Shin Tokudaiji), a liberal intellectual. The political situation having changed, Yamaoka is to be released from prison after five years but is now in extremely poor health. Hiroko intends to return to him, resume their former relationship and marry once his health recovers. This is anathema to Kono who still objects to his liberalist views and views himself as having a hold over Hiroko’s future as the head of her family and in having supported her financially.
Financial support is a cornerstone if not the full foundation of Kono’s position of entitled superiority over Hiroko and her family. Despite the melodramatic underpinning of the case at hand, the real questions are the ones defining the direction of the post-war world in pitting the feudal values of “duty” and “womanliness” against a modernising liberality that prizes freedom and equality above hierarchy and obligation.
Kono, perhaps to his credit, does not appear object to the idea of female lawyers and has indeed facilitated Hiroko’s rise to just such as position but otherwise affirms that “a woman’s duty is easy. All that is required of her is self-sacrifice”. The idea of “self-sacrifice” is one which is brought up in the closing speeches of the trial in which Hiroko makes an impassioned plea in the case of a mother, Moto (Mitsuko Miura), who, mad with grief, held her baby too closely and may have suffocated it. Kono’s argument is that Moto’s transgression is against nature and the social order, that she has “failed” as a woman in rejecting her maternity by murdering her child. He rejects the “extenuating circumstances” of her grief and desperation by painting her “crime” as a selfish one in choosing to save her own life rather than sacrifice herself on her child’s behalf. Insisting that she has “disgraced the morals of women”, Kono requests she be punished severely as an example to the others.
In refuting Kono’s argument, Hiroko not only restates the extenuating circumstances of the intense strain on Moto’s mental health but attacks his entire way of thinking in positioning “motherhood” as the primary female “duty”. She does not deny that there have been many wonderful stories of women who valiantly sacrificed their own lives for their families, but reminds the court that these stories have often been misused as a kind of propaganda in service of female oppression, that under the feudal system which militarists prized so highly women were little more than slaves to men with no rights or agency. Further more, she points to the corruption of the hierarchical society which has left Moto in such a difficult position following her husband’s early death as a result of an accident at the factory for which the factory paid but only until the end of the war at which time he was cruelly cast away like so many of his generation who had perhaps been similarly exploited to serve a similar idea of “duty” only this time to the state. Kono blames Moto, insisting that her “crime” occurred because her character is “weak”. Hiroko does not blame Moto at all but the society which placed her in such an impossible position and has all but broken her spirit.
The argument is between a fair and just society in which the law exists for the protection of the people, and an austere and cruel one in which the law exists to oppress and tyrannise. Kono, an arch and unreconstructed militarist, believes in the primacy of the law. He is rigid and uncompromising, branding Hiroko’s summation as “sentimental” and “romantic”, dismissing an “irrational” woman’s logic from his elevated position on the podium. As others point out to him, his way of thinking is outdated and his tendency towards an entitled assumption that it will eventually prevail through being the proper order of things is extremely misguided yet he clings fiercely to feudalistic values which have ensured power remains in the hands of people like him since time immemorial, uncompromising to the last.
Rather than focus on Moto and her trial, Mizoguchi and his scriptwriters Kogo Noda and Kaneto Shindo, return to the realms of melodrama in shifting into the domestic as Hiroko’s older sister Michiko struggles between the feudal duty to her husband (however much she appears to dislike him) and her love for her sister whose modern liberal way of thinking still strikes her as immoral. Michiko, it seems, was forced to sacrifice herself for her family in marrying Kono for financial support. The sisters’ mother, now committed to Hiroko’s way of thinking, willingly married her daughter off telling her never to return believing it to be the proper way of things. Having suffered so long in service of an ideal no longer current, Michiko gradually comes to the realisation that she now has a choice – she does not have to stay with a husband who she does not love and does not love her, she is free to leave him and live as a full and independent woman if that is her individual will.
Nevertheless, the slightly awkward framing perhaps casts the choices of Hiroko and her sister as being defined by their respective men – Hiroko swept along by Yamaoka’s socialist politics and Michiko by her husband’s conservatism. Both men are in different senses problematic – Yamaoka vindictive and unsympathetic to Michiko’s attempts to make peace, no more forgiving than Kono while also patronising in his last impassioned speech which places such great responsibility in Hiroko’s “tiny hands”. Nevertheless, Hiroko’s clearsighted fight not only for her own freedom but for a fairer, more compassionate society founded on the idea of a literal social justice in which the law exists in service of its people rather than to oppress them is remarkably forward thinking, moving beyond “propaganda” for the new regime to the better world so often envisaged by the post-war humanists.






 Kiju (Yoshishige) Yoshida is best remembered for his extraordinary run of avant-garde masterpieces in the late 1960s and early 1970s, but even he had to cut his teeth on Shochiku’s speciality genre – the romantic melodrama. Adapted from a best selling novel, Akitsu Springs (秋津温泉, Akitsu Onsen) is hardly an original tale in its doom laden reflection of the hopelessness and inertia of the post-war world as depicted in the frustrated love story of a self sacrificing woman and self destructive man, but Yoshida elevates the material through his characteristically beautiful compositions and full use of the particularly lush colour palate.
Kiju (Yoshishige) Yoshida is best remembered for his extraordinary run of avant-garde masterpieces in the late 1960s and early 1970s, but even he had to cut his teeth on Shochiku’s speciality genre – the romantic melodrama. Adapted from a best selling novel, Akitsu Springs (秋津温泉, Akitsu Onsen) is hardly an original tale in its doom laden reflection of the hopelessness and inertia of the post-war world as depicted in the frustrated love story of a self sacrificing woman and self destructive man, but Yoshida elevates the material through his characteristically beautiful compositions and full use of the particularly lush colour palate. An Autumn Afternoon (秋刀魚の味, Sanma no Aji) was to be Ozu’s final work. This was however more by accident than design – despite serious illness Ozu intended to continue working and had even left a few notes relating to a follow up project which was destined never to be completed. Even if not exactly intended to become the final point of a thirty-five year career, An Autumn Afternoon is an apt place to end, neatly revisiting the director’s key concerns and starring some of his most frequent collaborators.
An Autumn Afternoon (秋刀魚の味, Sanma no Aji) was to be Ozu’s final work. This was however more by accident than design – despite serious illness Ozu intended to continue working and had even left a few notes relating to a follow up project which was destined never to be completed. Even if not exactly intended to become the final point of a thirty-five year career, An Autumn Afternoon is an apt place to end, neatly revisiting the director’s key concerns and starring some of his most frequent collaborators.