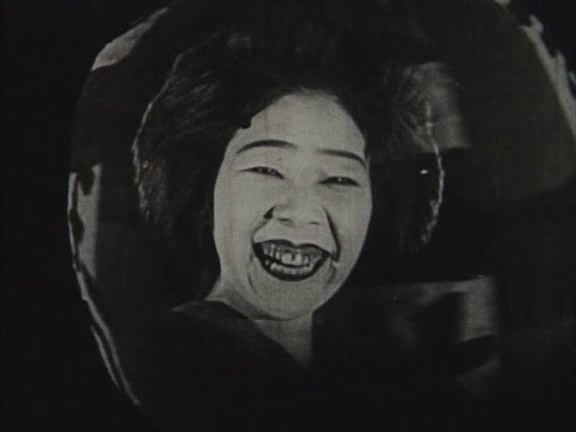
“Happiness is waiting for you” the melancholy heroine of The Dancing Girl of Izu (恋の花咲く 伊豆の踊子, Koi no Hana Saku Izu no Odoriko) is told by a man who truly loves her, though with his words all her hopes are dashed. Shot on location, Heinosuke Gosho’s 1933 silent is the first of several adaptations of the well-known Yasunari Kawabata story from 1926 and takes a number of liberties with the source material which are partly in keeping with the demands of contemporary cinema and partly an attempt to anchor it more firmly to the increasingly chaotic world of 1933 beset with both economic and political instability thanks to the global depression and Japan’s imperialist ambitions. The price of “happiness” it seems may be love, but perhaps stability as is much as you can ask for in an infinitely unstable world.
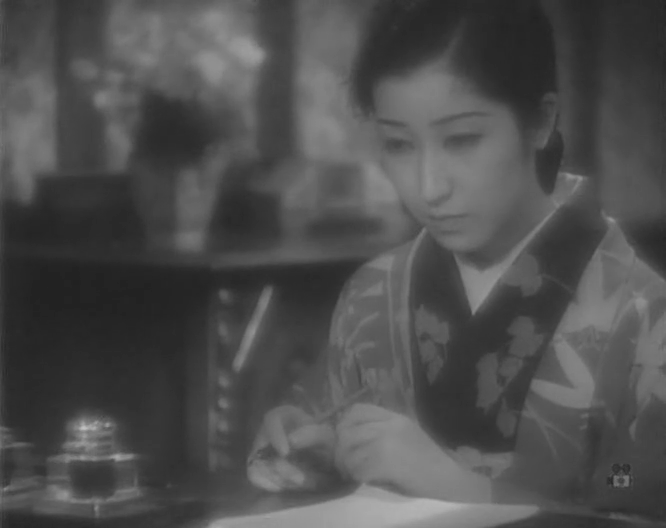
Nominally speaking, the hero of this tale is a young student, Mizuhara (Den Ohinata), through whose eyes we view the transitory nature of young love and the rigidity of a society which will in the end not permit its fulfilment. The “dancing girl” however is our primary focus. Kaoru (Kinuyo Tanaka) is the orphaned younger sister of Eikichi (Tokuji Kobayashi) who inherited a literal goldmine but squandered his inheritance and forced the whole family on the road to earn their keep as travelling players. Such people occupy a kind of underclass, victims of a prejudice against those who have no fixed abode and cannot easily be identified through association with a place or people. Kaoru admits that though she has learned to bear her way of life because at least she’s with her family, signs such as the one they find in a ditch to the effect that beggars and itinerant actors are not welcome in the town fill her with despair.
Mizuhara meets the actors when they have been unfairly accused of dumping the sign out of frustration (a child later vindicates them after confirming that it was a wandering priest who passed through shortly before). He wades into the fray to urge the angry farmers to exercise a little more patience and ends up agreeing to travel with the family to their next destination as he is himself engaged in a kind of holiday wandering around the picturesque countryside of the Izu peninsula (a popular activity for well to do students of the time). Unbeknownst to him they are already connected by mutual acquaintances in that a friend of Mizuhara’s, Ryuichi (Ryoichi Takeuchi), from the same university also lives in this town and is the son of the man, Zenbei (Arai Atsushi), who bought the goldmine from Eikichi after he went bankrupt.
The economic subplot concerns an amoral mining engineer, Kubota (Reikichi Kawamura), who apparently has a reputation as a “slave driver” and was responsible for starting the mine which Eikichi’s father owned, the implication being that it failed because of his exploitative business practices and has flourished under Zenbei’s more compassionate ownership in contrast to the picture Kubota is about to paint of him. Having apparently failed at several other endeavours, Kubota has sworn off mines but has convinced himself that he is “owed” something seeing as Zenbei’s mine is now a success and he was the one who found it. He tries to get something out of Ryuichi, but he is unconvinced and eventually offended, accusing of Kubota of blackmail when he insinuates that there was something improper about his buying the mine from Eikichi for much less than it was worth.
The film’s opening sequence which set up a subplot never resolved about a runaway geisha, however, showed us that Zenbei is as his name suggests a kindhearted man. He reported the geisha’s disappearance to the police not because she took off without clearing her debts but because he was worried for her safety, believing she may have been tricked into running off with an unscrupulous client. Kubota plants the seeds of resentment by convincing Eikichi that he was cheated out of the mine and is owed compensation. Eikichi, feeling humiliated, is determined to “negotiate”, but Zenbei tells him to give them his sister.
As will be revealed later, Zenbei’s intentions are honourable and he has no thought of replacing the geisha who ran away with Kaoru but wants to take her into his household as an adopted daughter. Eikichi, however, misunderstands but is prepared to sell his sister in order to pursue a pointless revenge against Zenbei by getting money to buy another mine and thereby become even richer. Mizuhara berated him for even considering the idea of trading his sister for money, but in the end even Eikichi only sees her as capital in his rage-fuelled desire to avenge his wounded male pride and sense of impotence. He failed as head of household in losing the family fortune and now has no intention of protecting his sister from the vagaries of the world.
Mizuhara once again intervenes and learns the truth from Zenbei, that he had been a friend of Eikichi’s father’s and has always been trying to look out for them but has recently lost patience with Eikichi who has already borrowed a lot of money from him. Zenbei is minded towards tough love, convinced his well-meaning attempts to help have only enabled Eikichi’s financial fecklessness. He doesn’t see why Kaoru should pay for his mistakes and has been putting some of the proceeds from the mine into a savings account in her name, hoping also that she may one day marry his son Ryuichi. Mizuhara is at once crushed by the painful goodness he sees in front of him, knowing that his love for Kaoru is now not only impossible but perhaps selfish. All he can do for her now is get out of the way so that she can be saved from the harsh life of an itinerant player, restored to her previous class status, and given the most elusive of all prizes in this chaotic age, stability.
Zenbei’s plan for Kaoru is in itself a kind of miracle, the best she could ever hope for, but it’s also a minor tragedy in that it both robs her of any kind of agency to make her own choices and destroys the possibility of a romantic future with Mizuhara. To accept everyday comfort and safety, she must resign herself to giving up her love. Mizuhara asks her to do just that in an altruistic act of selflessness which recognises that without money he is powerless to help her. He’s not the one she loves (and we have no idea how he might feel about it), but Ryuichi seems to be a good and kind man, like his father Zenbei who is perhaps the face of compassionate, paternalist capitalism. The world is too chaotic for romance, but there is kindness enough if you’re lucky enough to find it, and if stability is all there is perhaps sorrow is easier to bear than hunger.