
An angst-ridden medical student wrestles with truth and responsibility while drawn into a toxic relationship with a childhood friend and trying to avoid the estranged mother he resents in Masahiro Shinoda’s dread-laden melodrama The Petrified Forest (化石の森, Kaseki no Mori). Based on a novel by Shintaro Ishihara who later became a very conservative mayor of Tokyo and made his name with a series of “Sun Tribe” novels centring on the nihilistic hedonism of wealthy post-war youth, Shinoda’s noirish drama paints contemporary Tokyo as a duplicitous place in which hate is the only possible emotion and self-delusion the only path out of existential loneliness.
Haruo’s (Kenichi Hagiwara) first conflict, however, is with the medical profession. He objects to the old-fashioned methods of his professor, Miyaji (Torahiko Hamada), who adopts the position of the physician as god only giving his patients the information he thinks they should have rather than the truth. A young boy, Kazuhiko (Masami Horiuchi ), is brought in with an aggressive brain tumour. Given how how quickly it regrows, there is a possibility that the boy cannot be cured while operating will likely mean he will lose his hearing. Though Miyaji knows all of this, he continues to give false reassurance to the boy’s mother, Kikue (Masako Yagi), even after making a snap decision on the table to excise the tumour knowing it will leave him deaf telling her that her son’s hearing might come back in time. Pressed for an answer, Haruo gives her the more honest prognosis that it “might”, “if he’s lucky”, but resents himself for “lying” knowing that Kazuhiko will be deaf all his life and the tumour may still recur. One of the reasons he wants Miyaji to tell the truth is so that the family can accept the situation and start working on the best ways to help Kazuhiko adjust, but Miyaji refuses to explain and in fact threatens to fire him if he won’t do as he’s told.
This resistance to a male authority figure might explain why he identifies so closely with childhood friend Eiko (Sayoko Ninomiya) now in Tokyo working at a barber’s offering male beauty treatments. Eiko is being sexually harassed by her middle-aged boss who is jealous and possessive. At one point she claims that he beat her and locked her up in a cupboard for two days after she told him she had slept with Haruo. The pair agree that he boss needs to die, rebelling against his corrupt and patriarchal authority. ”When you hate you must hate all the way” Haruo insists, explaining that the human race is “petrified”. They can only hate and loathe and lie to themselves in order to bear it. Haruo suggests they’ll eventually come to hate each other, but Eiko is certain that he’s her one exception though as will be revealed hate is eventually where they will end up.
Fascinated by a high tech pesticide supposedly discovered by the Germans while they were testing poisonous gases but perfected by Japan Pharma, Haruo decides to use it poison to Eiko’s boss suggesting she put it in nail varnish and offer him a manicure. But once the deed is done he finds himself conflicted, unable to live with himself as a murderer which he now is seeing as he was present and applied the gauze soaked in the poison to the boss’ face while “treating” him after he had been “taken ill”. He distances himself from Eiko who irritates him by bringing over her hoover, somehow confused by her intention to move in now that they are married not least by their crime. Eiko, however, allies herself with his estranged mother Tatsuko (Haruko Sugimura) who is desperate to live with Haruo as it turns out by any means possible.
There is an undeniable whiff of misogyny in the depiction of the two women, Eiko less damsel in distress than wilful manipulator and Tatsuko a classic overbearing mother though one apparently indifferent to her other two children including an apparently doting younger son. Haruo is caught between the two while otherwise drawn to Kikue in part because of her relationship with her son laying bare the apparent mother complex which defines his life as Eiko eventually points out calling him a coward who secretly craves his mother’s approval. Haruo’s resentment towards Tatsuko stems from having caught her with another man, his reaction both sexual jealously and puritanism unable to forgive for the transgression of adultery. Yet history later repeats itself, Kazuhiko who is at that point deaf walking in on Haruo and his mother. Haruo hugs him and covers his eyes only for the boy to later lose his sight and Kikue to go out of her mind wailing that she has destroyed her son through her sexual transgressions.
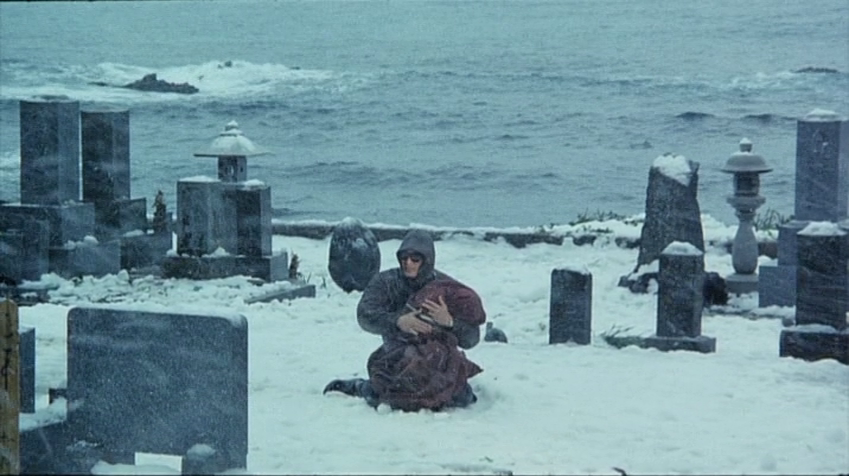
Kikue had taken Haruo to a strange cult where she hoped Kazuhiko would be cured though he wouldn’t enter the church and later got into a conversation with the monk who is a former doctor but now believes medicine is a con because it cannot offer you salvation tacitly agreeing with Haruo’s assertion that doctors too are dishonest. This tendency to hate has rendered everyone lonely, Tatsuko’s daughter reminding her that she is lonely too even with her husband and children while Tatsuko later cruelly uses Eiko’s loneliness against her as a tool of manipulation. “Eiko trusted me too much” she explains, her attempt at female solidarity and forging a bond through their shared desire to possess Haruo obviously failing to overcome Tatsuko’s matriarchal machinations. The eerie blue colour of the poison vial, mirrored in the nebuliser forever used by Tatsuko, seems to loom behind them as a reminder of human loathing while mother and son are frequently caught in multiple mirrors in an echo of their duplicity yet in the end as Tatsuko says they share the same sin and it seems Haruo will never really be able to escape the matriarchal net.










 Never one to be accused of clarity, Seijun Suzuki’s Capone Cries a Lot (カポネおおいになく, Capone Ooni Naku) is one of his most cheerfully bizarre movies coming fairly late in his career yet and neatly slotting itself in right after Suzuki’s first two Taisho era movies,
Never one to be accused of clarity, Seijun Suzuki’s Capone Cries a Lot (カポネおおいになく, Capone Ooni Naku) is one of his most cheerfully bizarre movies coming fairly late in his career yet and neatly slotting itself in right after Suzuki’s first two Taisho era movies,