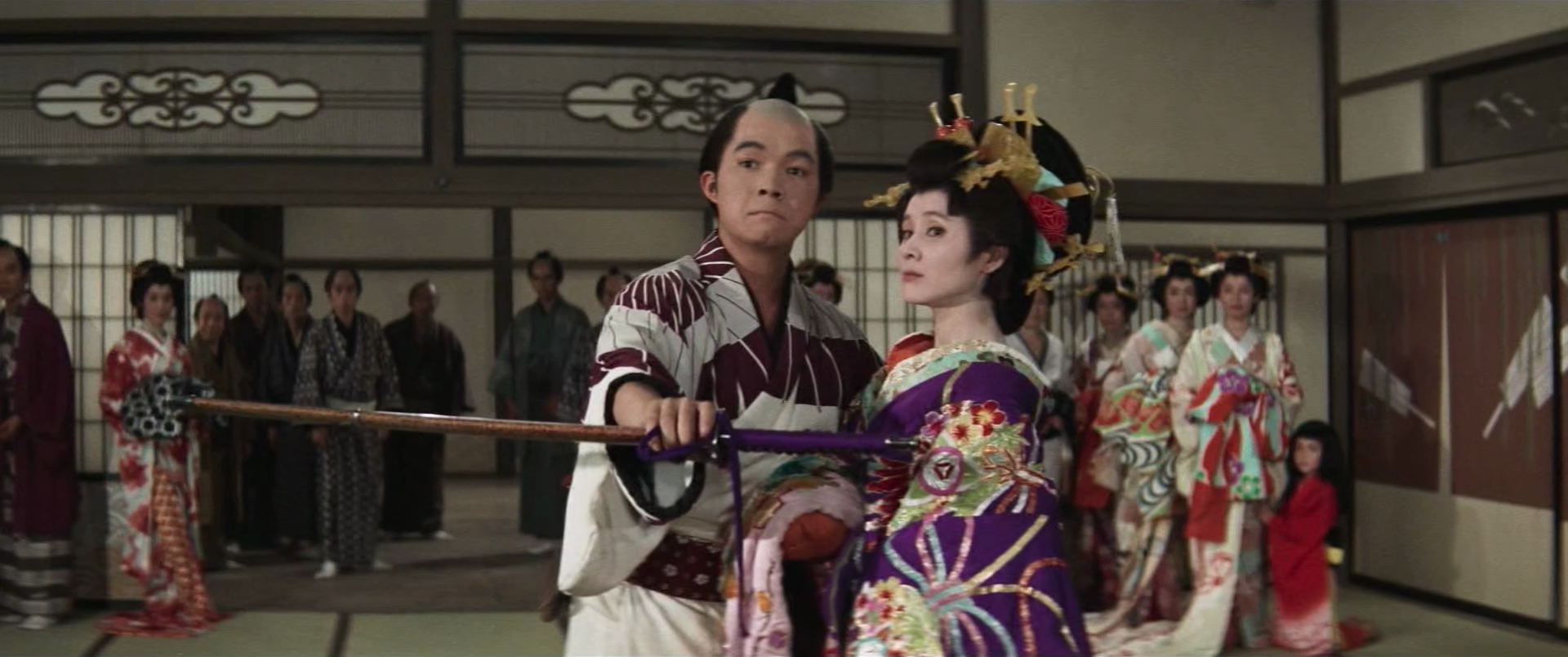
Kyu Sakamoto was a hugely popular singing star in the 1960s best known internationally for the smash hit Ue wo Muite Aruko (Sukiyaki) which, somewhat incongruously, features in this jidaigeki comedy, Kyu-chan Draw Your Sword (九ちゃん刀を抜いて, Kyu-chan Katana wo Nuite), directed by one of the masters of the samurai movie, Masahiro Makino. Adapted from the novel by Ippei Okamoto, the film is essentially a vehicle for Sakamoto as indicated by the inclusion of his name in the title even though he plays a character called “Sangoro”.
The joke is that Sangoro is incredibly lazy and can hardly lift his head off the pillow while his ageing parents are struggling to feed themselves. If they don’t find a way to get him working soon, they’ll all starve to death but Sangoro seems incapable of understanding. The parents try to think up various jobs he could do without having to exert himself and eventually come up with Kyokaku, or “town knight”, a man about town of the Edo era somewhere between street tough and vigilante. In fact he even ends up meeting some legendary characters such as Banzuiin Chobe (Eitaro Shindo) who became a kind of Robin Hood figure in later literature standing up for the common man against the abuses of the samurai class.
When he goes off to the city to become a Kyokaku because he figures starving to death would be too much effort, Sangoro’s father cautions him not to be too lazy to draw his sword even though it’s rusty and unlikely to do much damage. Sengoro does, however, take his ambition seriously and is keen to make a name for himself in Edo which he first does by becoming the blood brother of Gonbei (Chiyonosuke Azuma), one of Banzuiin’s men. Though his clumsy attempts to fight him don’t bode well for Sangoro’s career, Gonbei takes him on precisely because he’s fun to have around even if he is a bit useless and sometimes you need guys like that too. Introducing him to area’s top courtesan Takamado (Yoko Minamida), they hope to set the cat among the pigeons with a local gang that’s been harassing them led by the irritating Mizuno (Fumitake Omura) and Shirogoro (Koshiro Harada).
Though the film may be, in a way, a sort of satire poking fun at aimless post-war youth that lacks ambition in comparison to their parents’ generation who bore the brunt of wartime privation. Naive and childish, Sangoro is a well-meaning bumbler, but Takamado unexpectedly likes him precisely for these qualities. She hates men like Mizuno who are obsessed with proving their masculinity and finds it refreshing that Sangoro is not afraid to show his weakness. Just like Gonbei, she appreciates him not for his command of the sword or imposing air of authority, but simply because he’s an uncomplicated good person and fun to be around.
Mizuno and Shigoro are, by contrast, cruel and abusive Tokugawa vassals, who, it’s implied, have a habit of murdering sex workers during their New Year endurance tests. Sangoro is keen to save a young woman, Omitsu (Yumiko Kokonoe), after her father did him a favour and explained he needed 25 ryo to buy back her contract after she agreed to sacrifice herself to get the money for her mother’s medical treatment. Which is to say, she’s the opposite of Sangoro. It turns out that Takamado has a sad story of her own staged by Makino using kabuki-esque sets and effects to dramatise her flashback as she explains her samurai father took his own life after a prisoner he was watching disappeared. Though in another film this might lead to a violent confrontation challenging the evil samurai, in this version a bizarre misundersanding is revealed to have caused the death of Takamado’s father leading to another act of levelling as the supposed villain agrees to give them his secret recipe for pickles with an exclusive license to manufacture it for three years before it’s essentially made open source for the good of the people. Thus Sangoro essentially becomes a shopkeeper and releases both Omitsu and Takamado from their position as indentured sex workers, restoring both their birthright and their freedom basically by being nice and the right kind of righteous while Mizuno and Shigoro just end up embarrassed when all their posturing and obsession with their samurai status appears to mean little in a world in which the merchant has indeed become king.