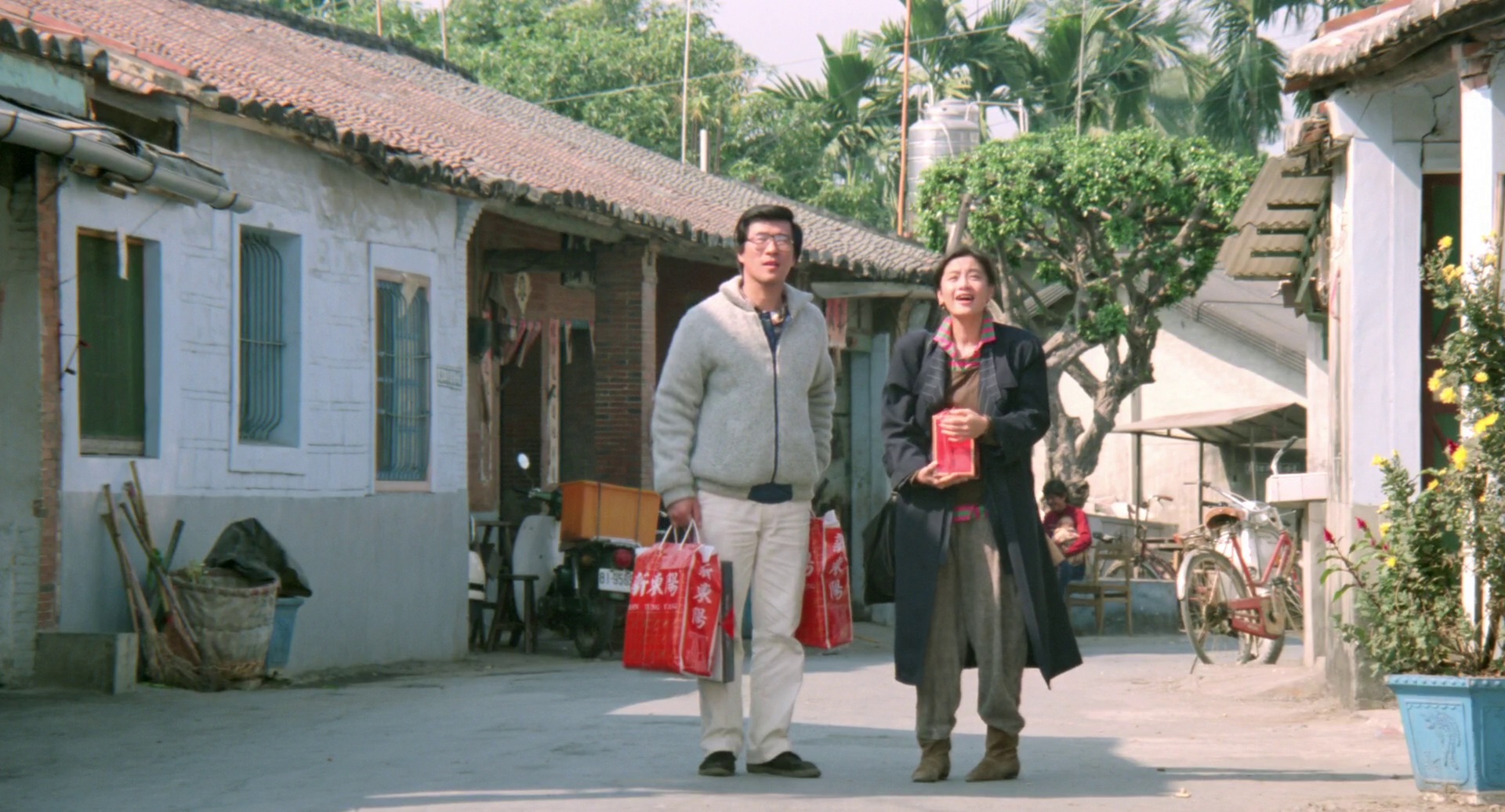
After becoming pregnant by her married lover, an otherwise independent young woman decides she must find a husband so that her baby will be legitimised but plans to divorce him a year later in Chen Kun-Hou’s charming Taipei-set rom-com, My Favourite Season (最想念的季節, zuì xiǎngniàn de jìjié). These contradictions perhaps express those at the centre of a changing society as the heroine temporarily shackles herself to a weak-willed man but finds herself both bonding with him and resentful of his attempts to control her, while the relationship itself continually straddles an awkward line.
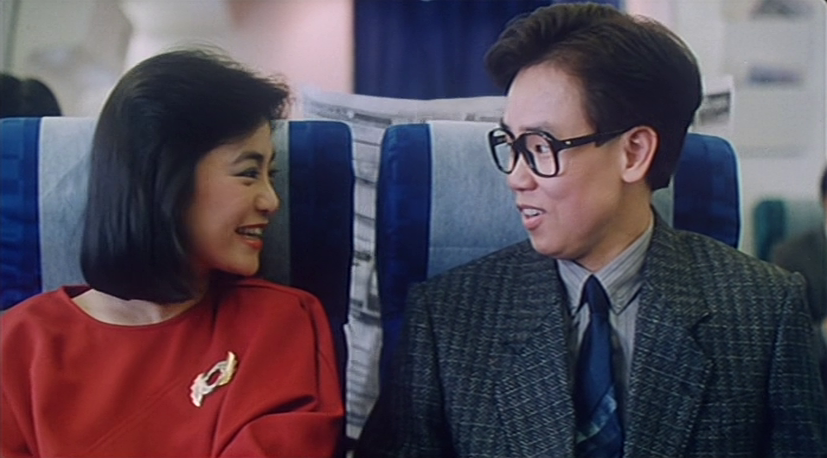
Pao-liang (Jonathan Lee Chung-shan) is a somewhat nerdy guy who runs a print shop and has become a guardian to his niece because his sister and her husband are struggling artists. Incredibly superstitious, he insists he won’t get married before the age of 30 because it would be bad luck, but is roped into Hsiang-mei’s (Sylvia Chang Ai-chia) scheme by a friend who turned her down. Pao-liang tries to turn her down too, but is also struck by her beauty, his own improbable luck, and a possibly genuine emotional connection the pair may share even though they are in other ways opposites.
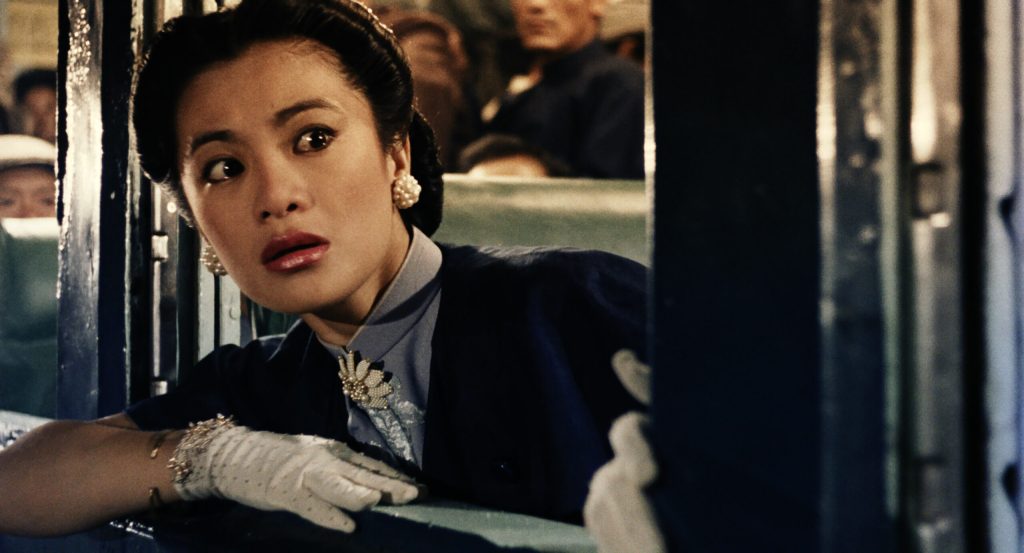
Hsiang-mei works as a journalist for a fashion magazine and has more sophisticated tastes as well as a looser connection to money than the penny-pinching Pao-liang who, as the saying goes, knows the cost of everything but the value of nothing. He doesn’t like it when Hsiang-mei spends her own money on things she wants and insists on keeping a running tally of mutual expenses. When his sister asks him for a loan to tide her over, he immediately refuses despite having a large amount in his bank account, partly because he’s mean with money and partly because he’s essentially selfish. Hsiang-mei gives it to her instead, which annoys Pao-liang on several levels because he realises it’s made him look bad while he is now further indebted to Hsiang-mei.
She, meanwhile, is from a small town and came to Taipei for a better life. The only girl in her family, Hsiao-mei strives for independence and ironically wanted a husband to secure it so she could have her baby and raise it on her own. As her brother says, “she does what she wants,” but seemingly hadn’t really thought through her plan assuming it would all go smoothly and she and Pao-liang could essentially hang out for a year and then bring the arrangement to an end. She picks Pao-liang partly because they do seem to get on, and possibly because she thought he’d be easy to manage, but is lucky in her choice of man that he presents little danger to her.
He is, however, petty and patriarchal in his mindset. He’s both attracted to Hsiang-mei and resentful of her strong will and independence while also small-minded and incapable of direct communication. It’s obvious that he wants this arrangement to continue, but often acts in ways that endanger it and lashes out at Hsiang-mei rather than explaining how he feels. When Hsiang-mei returns upset having met up with her married lover, Pao-liang shouts at her and accuses her of embarrassing him by sleeping with another man. He does something similar when she encounters unexpected tragedy, blaming and berating her in place of offering comfort even if his cruelty is motivated by frustrated affection.
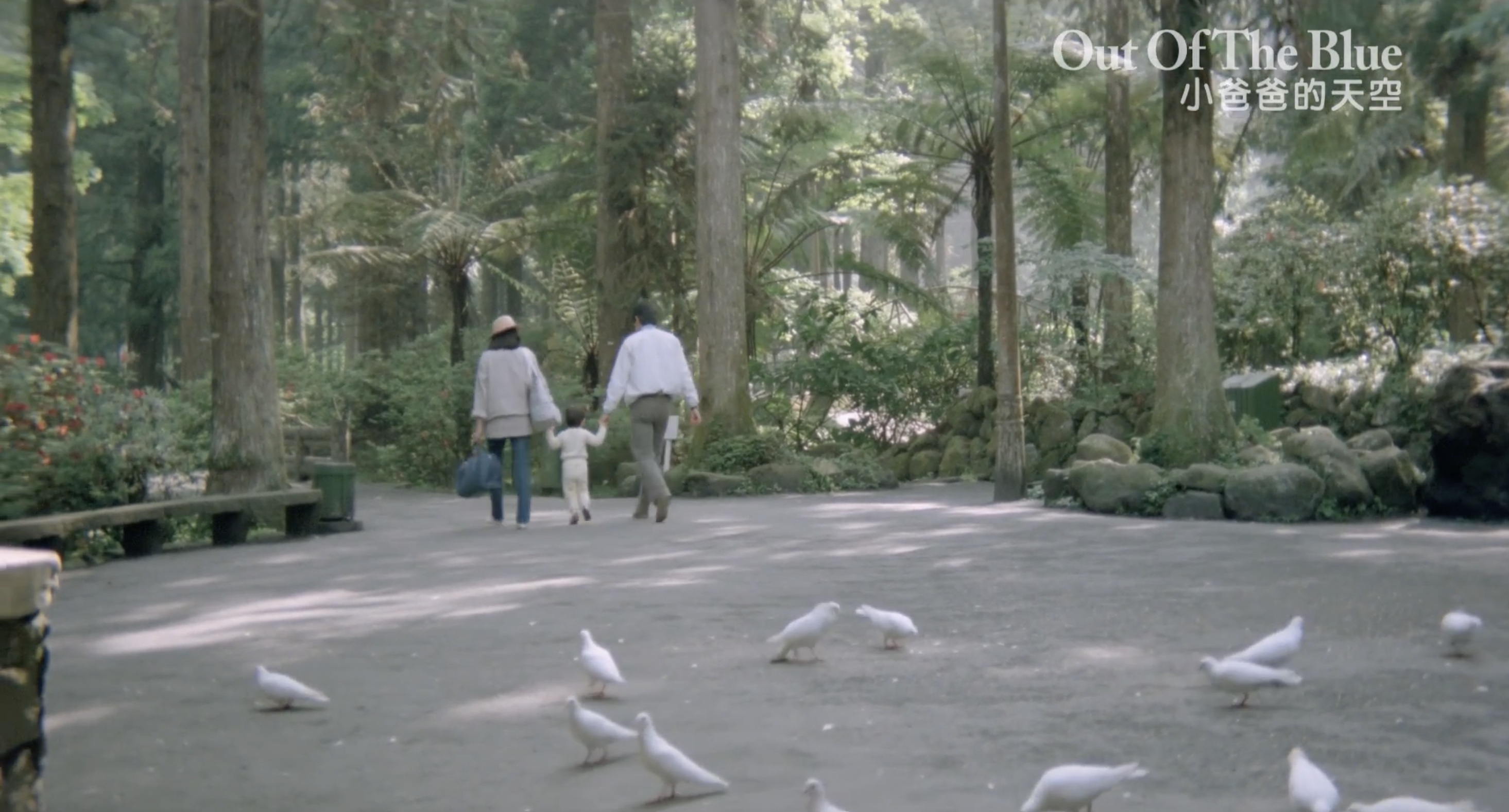
But Hsiang-mei is in some ways the same. She doesn’t really say what she wants either or acknowledge that she has grown fond of Pao-liang and his niece. She’s fiercely independent, but felt she still needed to have a husband to have a baby after having an affair with a man who was already married so was to her the ideal boyfriend because he wouldn’t tie her down. She buys a lamp for Pao-liang’s place because lamps make a place a home, but Pao-liang doesn’t want it or approve of the expense while simultaneously insisting on paying for half of it because it’s for a “communal” area. He’s still intent on keeping score and isn’t ready to accept that he and Hsiang-mei live in the house together so everything belongs to them “communally” as a couple. On a baseline level, he won’t cede his space to her nor acknowledge that she still has the upper-hand in this relationship even as the pair inevitably draw closer. Chen’s vision of 80s Taipei is warm and sophisticated as Pao-liang spends his time dancing with the old ladies in the park and loses his keys at opportune moments or drives his car into a ditch but even despite his pettiness and ineffectuality, can still find love and the courage to chase it if somewhat passive aggressively.
My Favorite Season screened as part of the BFI’s Myriad Voices: Reframing Taiwan New Cinema.
Trailer (Traditional Chinese / English subtitles)