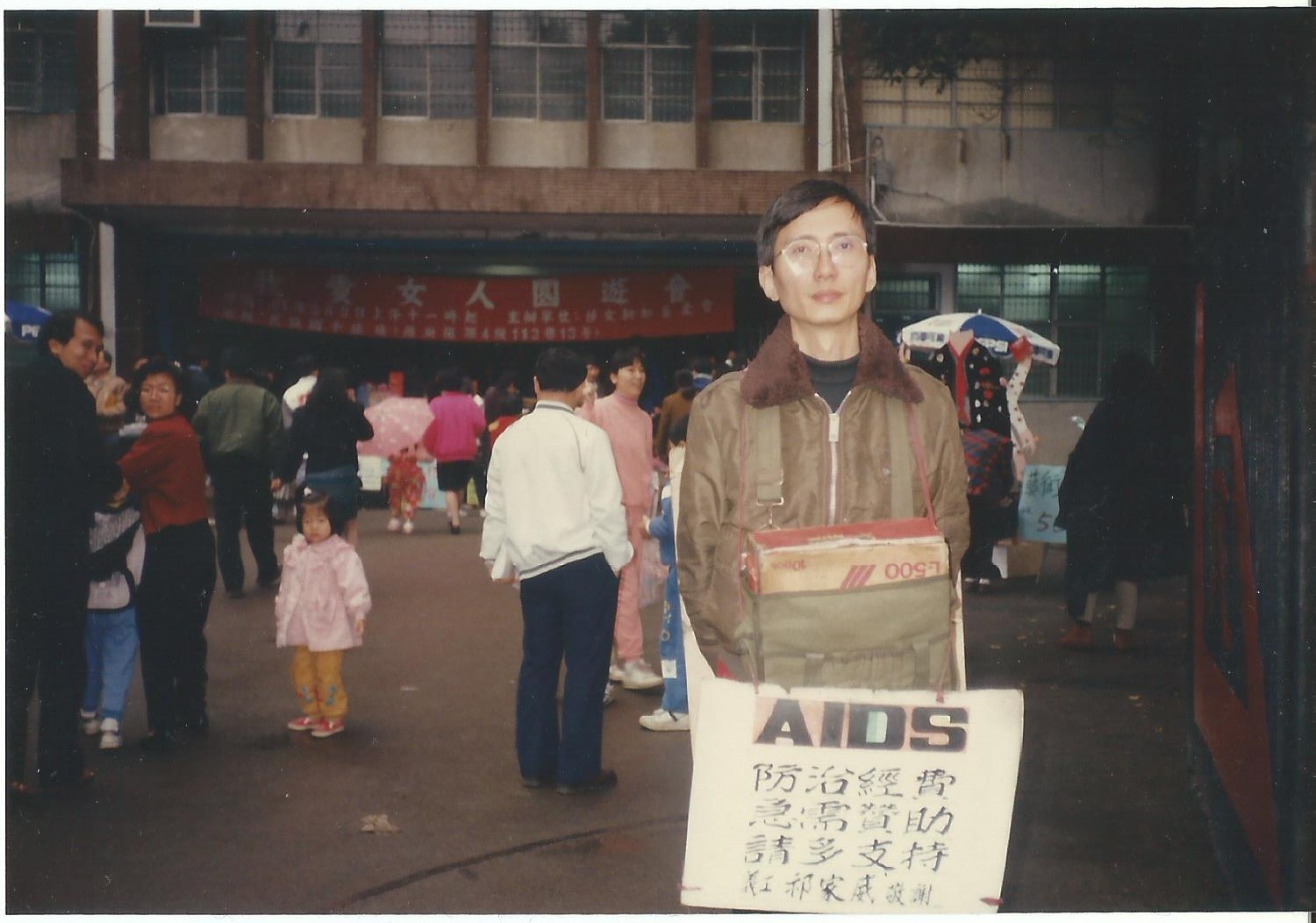
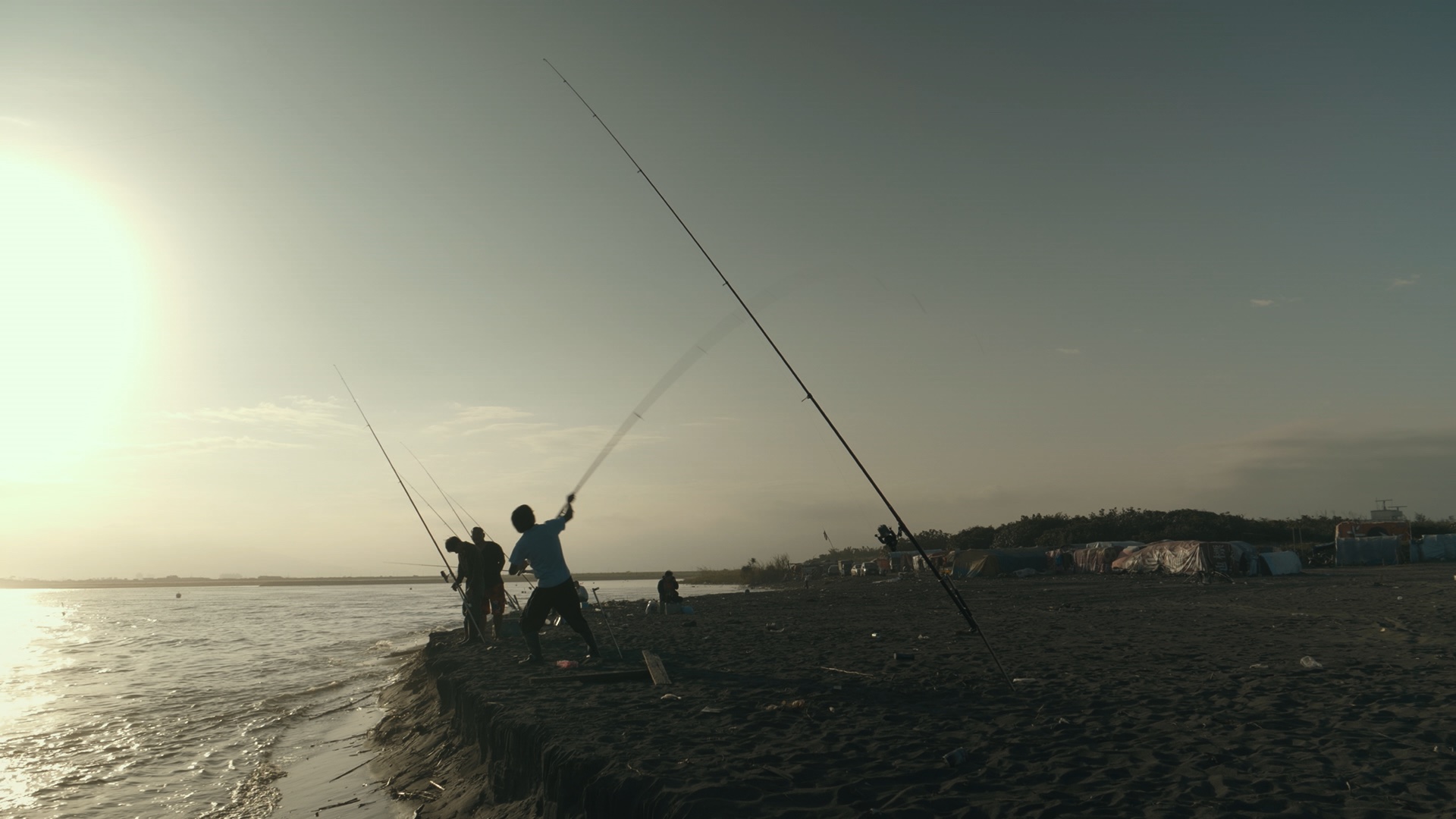
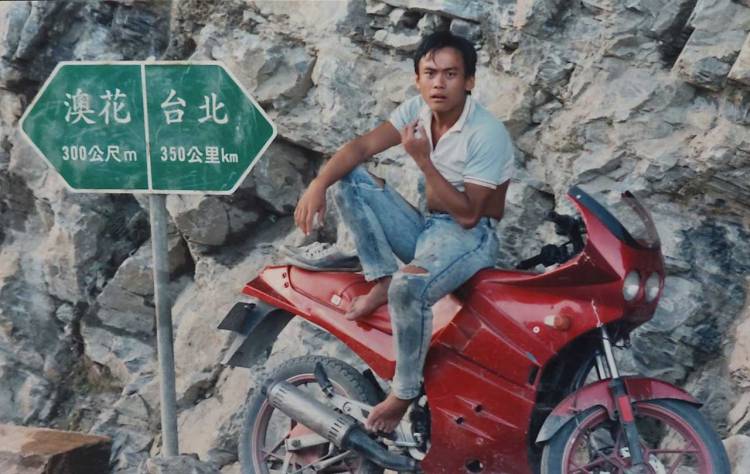
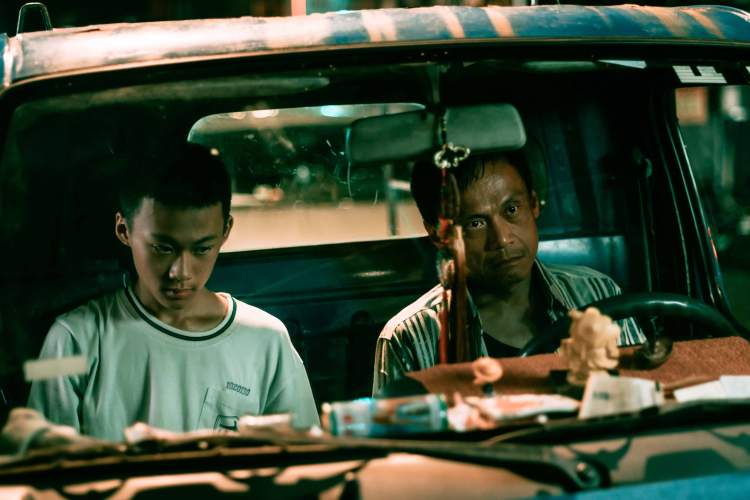
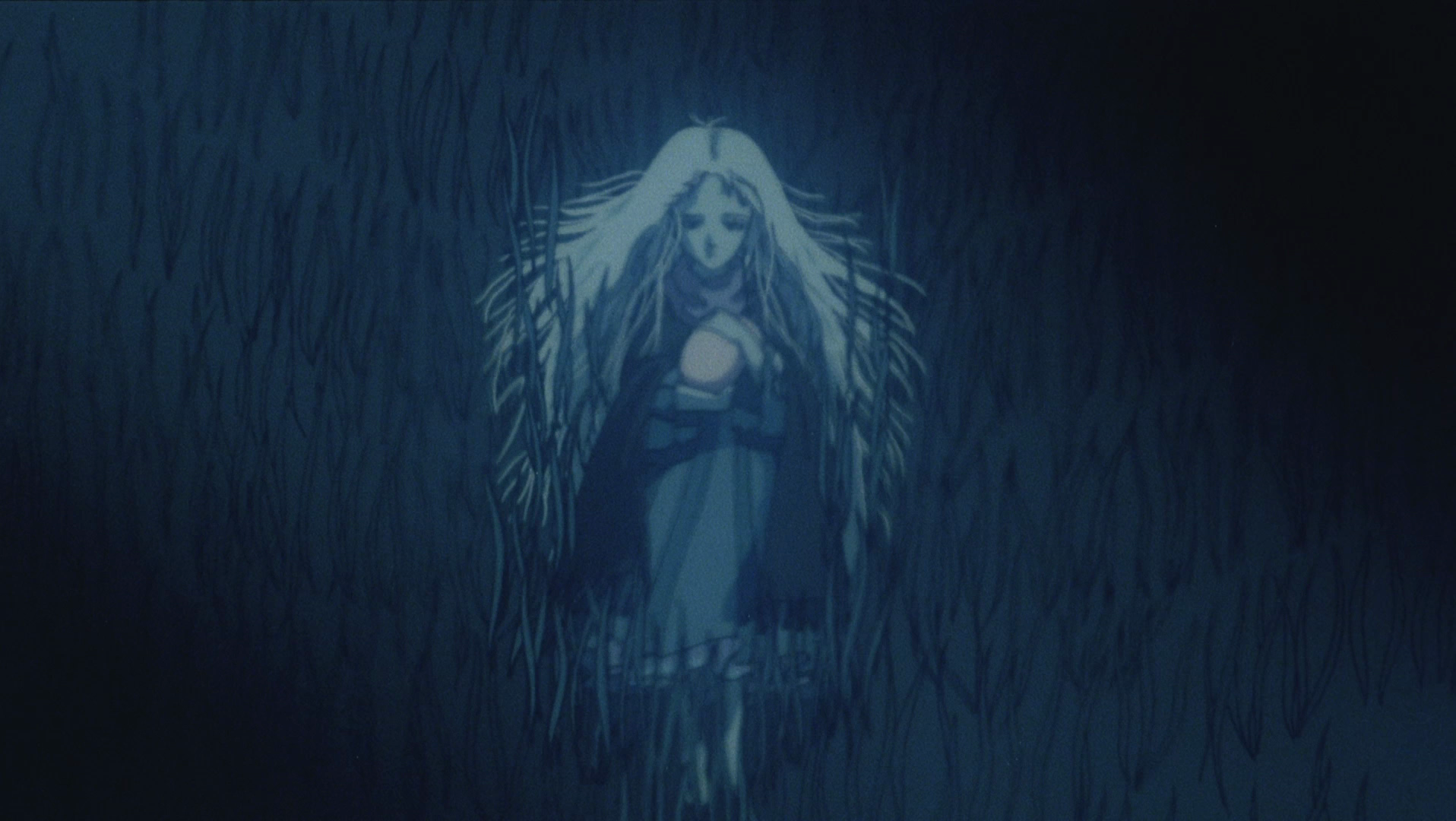
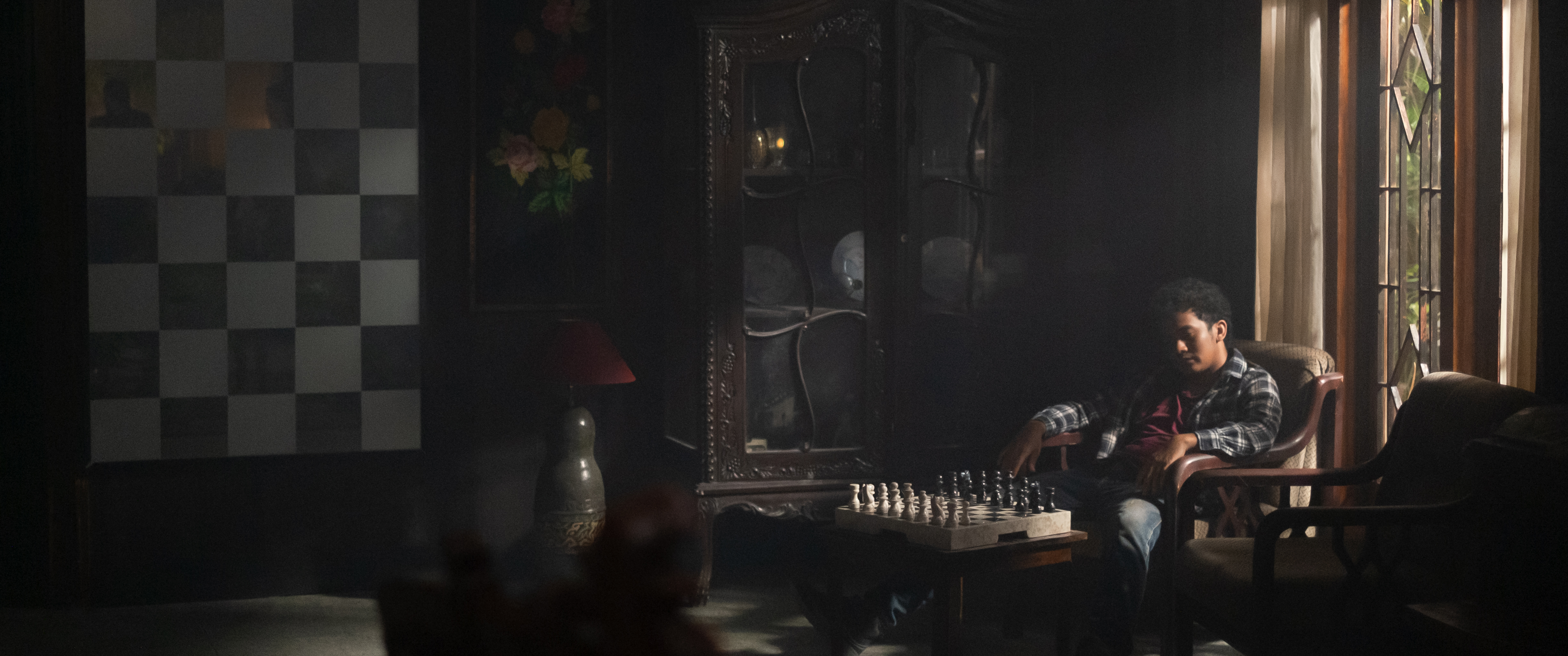Two indigenous men find themselves searching for a place to belong in a changing Taiwan in Huang Ming-chuan’s poetic drama The Man From Island West (西部來的人, xībù lái de rén). A folktale told at intervals throughout the film sees a curious young man leave his community and find another only to be cast out, return, and be cast out again. While one young man dreams of escaping the village he sees as backwards and restrictive, another who had left longs to return but finds that one place is much like another and neither have much place for him.
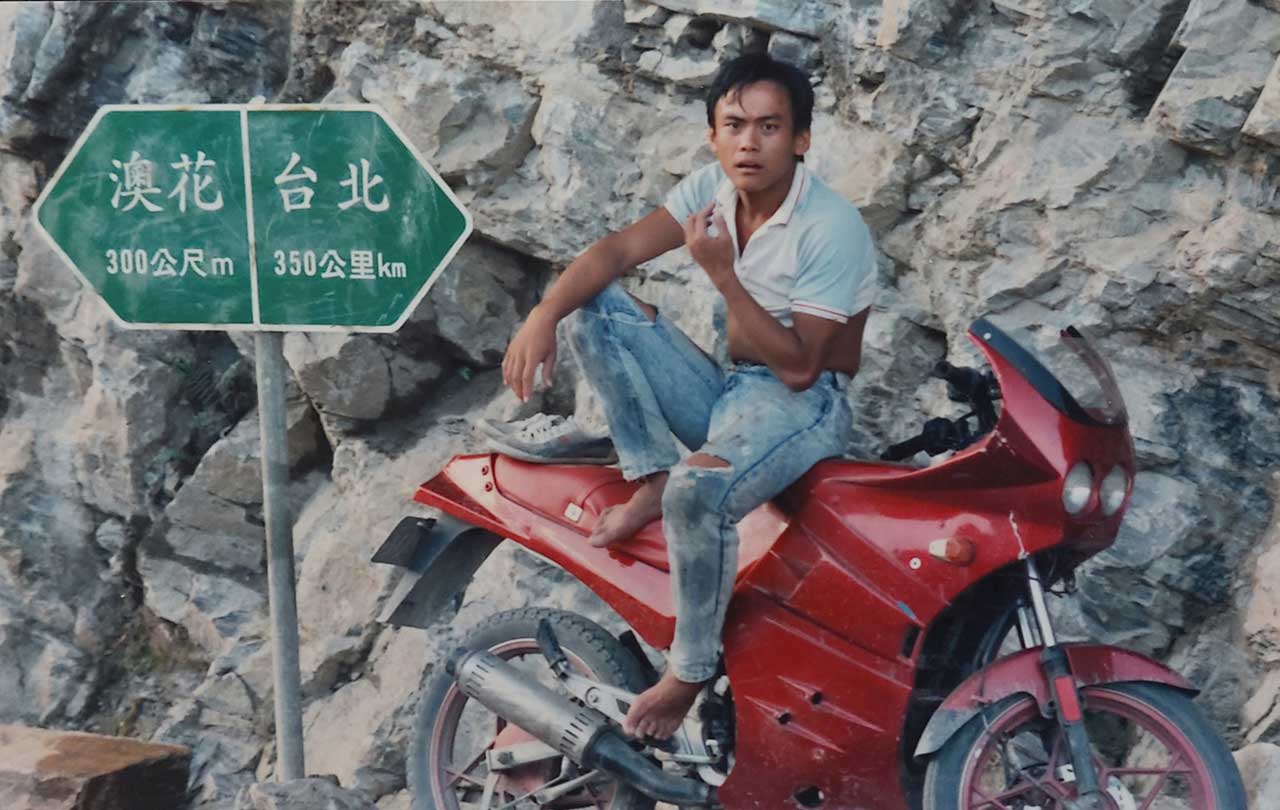
Beginning and ending in a fiery crash, the film opens with a limping Ah-Ming (Wu Hong-ming) having survived a car accident assumed to be a suicide attempt. Keeping himself to himself, Ah-Ming finds refuge with a local man and his hotheaded son, Ah-Chuan (Chen Yi-wen), who has a job at the local quarry as do most of the men of the indigenous community who have not already left for the city. Though the pair generate something like an awkward friendship, it is soon disrupted by the return of Hsiu Mei (Shaw Tswe-fen), Ah-Chuan’s former girlfriend, who has returned after five years in Taipei now apparently a rich woman.
“There’s only one thing that mountain girls can do in Taipei” Ah-Chuan explains, “They never come home to stay. It affects them all in the same way”. Ah-Chuan may long to go to Taipei himself, but cannot accept the returned Hsiu Mei, reminding her that she is not the same girl she was five years ago rejecting her both because of her involvement with sex work and because of her urbanisation. As we discover, Hsiu Mei is on the run from trouble in the city and had perhaps thought to find refuge back in the village free from the corruptions of urban life only she gradually realises that she doesn’t fit in there anymore either. As Ah-Chuan had said, she’s not the girl she was before and the men of the Atayal community are not so different from those in Taipei who refused to recognise her humanity seeing her only as a commodity to be used and discarded.
“There’s no difference between here and Taipei” Ah-Ming agrees, “all cold, loneliness, dreams of faraway places, one always awakes to harsh realities”. Telling his own story through that of the folktale, Ah-Ming reflects on his mountain childhood, sent away to the city by a father who wanted a better life for his son but is said to have wasted away with his eyes open waiting his return. For whatever reason, it seems that city life did not suit Ah-Ming and he longs to return to the simplicity of the village but is still seen as somehow other unable to reintegrate into its society living first in a chicken coup and then symbolically in a disused tunnel trapped between one place and another.
When she makes the decision to leave, Hsiu Mei gives her red scooter to Ah-Ming in some sense giving him the possibility of movement which it seems he does not really take up but is in any case prevented from doing so when Ah-Chuan steals the bike from him. Yet as his father points out, Ah-Chuan does not think things through. All he knows is quarrying, he is not the sort of boy who could survive in the city but nor is he an Atayal man. As his father laments, they used to hunt in the forests all day long but now all they do is cut stone, caught between tradition and modernity but discovering only ruin and exploitation. Ah-Chuan snatches a basket weaved by his father which is also like that in which Ah-Ming used to ride on his father’s back and takes off in anger but on re-encountering Hsiu Mei is forced into the realisation that he will not leave the village and this life is all that he will have. A poetic, lo-fi epic, Huang’s indie drama is also perhaps in its way about Taiwan after martial law, seeking a home and an identity in searching for its roots though it seems for Ah-Chuan and Ah-Ming all there may be is a kind of restless wandering in the yearning for an elusive sense of belonging.
The Man from Island West screens 17th October as part of this year’s Taiwan Film Festival Edinburgh.
Original trailer English subtitles