
Kei Kumai’s three-hour epic of human engineering The Sands of Kurobe (黒部の太陽, Kurobe no Taiyo) opens with a titlecard to the effect that the film testifies to the courage of the Japanese people who brought the nation back to life after the war. Partly produced by Kansai Electric Power along with the production agencies of stars Toshiro Mifune and Yujiro Ishihara, the film is therefore somewhat conflicted, part bombastic celebration of Japanese engineering skill and ambivalent critique of the wilful decision to place success above all else including the welfare and safety of ordinary workers.
This critique is most evident to the flashbacks to the construction of Kuro 3 in 1938 which as many point out was conducted by the military under brutal and primitive conditions. The construction of the new Kurobe hydroelectric dam, by contrast, is a much more modern, enlightened affair in which workers have proper equipment and are not simply hacking at rocks with pickaxes wearing only a vest. But then as the conflicted Takeshi (Yujiro Ishihara) points out, it’s all effectively the same. Just because no one is pointing a gun at their heads, it doesn’t mean the men actually building the dam aren’t being exploited rather simply pressured by a vague notion of national good that they should be ready to lay down their lives. Could it be that “prosperity” is worse thing to die for than “patriotism”, especially when it appears as if your employer cares little for your physical wealth and economic wellbeing simply pledging that they will support the families of men killed during the dam’s construction.
That there will be deaths seems inevitable. The man placed in charge of building a tunnel through the mountain, Kitagawa (Toshiro Mifune), is haunted by the vision of a man falling from a cliff that he witnessed when they first hiked to the dam site. He originally described the project as “crazy” and wanted to resign but was convinced to stay on. Kitagawa is himself fond of insisting on safety first where others are minded to cut corners, but also troubled by domestic issues in the film’s sometimes insensitive use of his daughter’s terminal leukaemia as a mirror for the dam project in considering what is and isn’t possible through human endeavour. The suggestion is that Kitagawa wants to believe the miracle of the dam is possible because needs to keep believing in a scientific miracle that can save his daughter, though obviously even if it is ultimately possible to build this dam that’s designed to fuel the post-war rocket to economic prosperity there are limits and unfortunately decades later we have still not found a cure for cancer though treatment may be more effective.
Takeshi meanwhile has a similar battle with his hard-nosed father whose devotion to the dam project he describes almost like an addiction, suggesting that he values nothing outside of tunnelling and is willing to sacrifice everything in its name including the lives of himself and others. A flashback to to 1938 reveals that he asked his own teenage son to place dynamite and inadvertently caused his death though lax safety procedures which is the understandable reason why his wife eventually left him taking Takeshi with her. But the strange thing is for all his original opposition, Takeshi too is later captivated by the immensity of the challenge if also wary that the workers are falling victim to the same sickness as his father and are still being exploited by those like him who expect them to offer up their lives while paying them a pittance and complaining when the project does not proceed along their schedule.
The almost nationalistic, bombastic quality of the film seems at odds with some of Kumai’s previous work save the discussion of the building of the 1938 tunnel though this largely serves as a contrast to imply that this time is different because they’re doing it for love of country rather the forced patriotism of the militarist past. Kitagawa justifies himself that if they don’t build the dam, economic prosperity will stall, companies will go bust, and people will lose their jobs but it seems somewhat hollow in the knowledge many men are certain to die while building this dam. Kumai undercuts the bombast with a series of scenes shot like a disaster movie in which supports collapse and the tunnel floods, or men are hit by falling rocks, eventually closing on an ironic Soviet-style statue dedicated to the labour of the workers that seems to question the immense loss of life along with the destruction of the natural beauty of Mount Kurobe but cannot in the end fully reconcile himself, torn between a celebration of human endeavour and its equally human costs.
Original trailer (no subtitles)



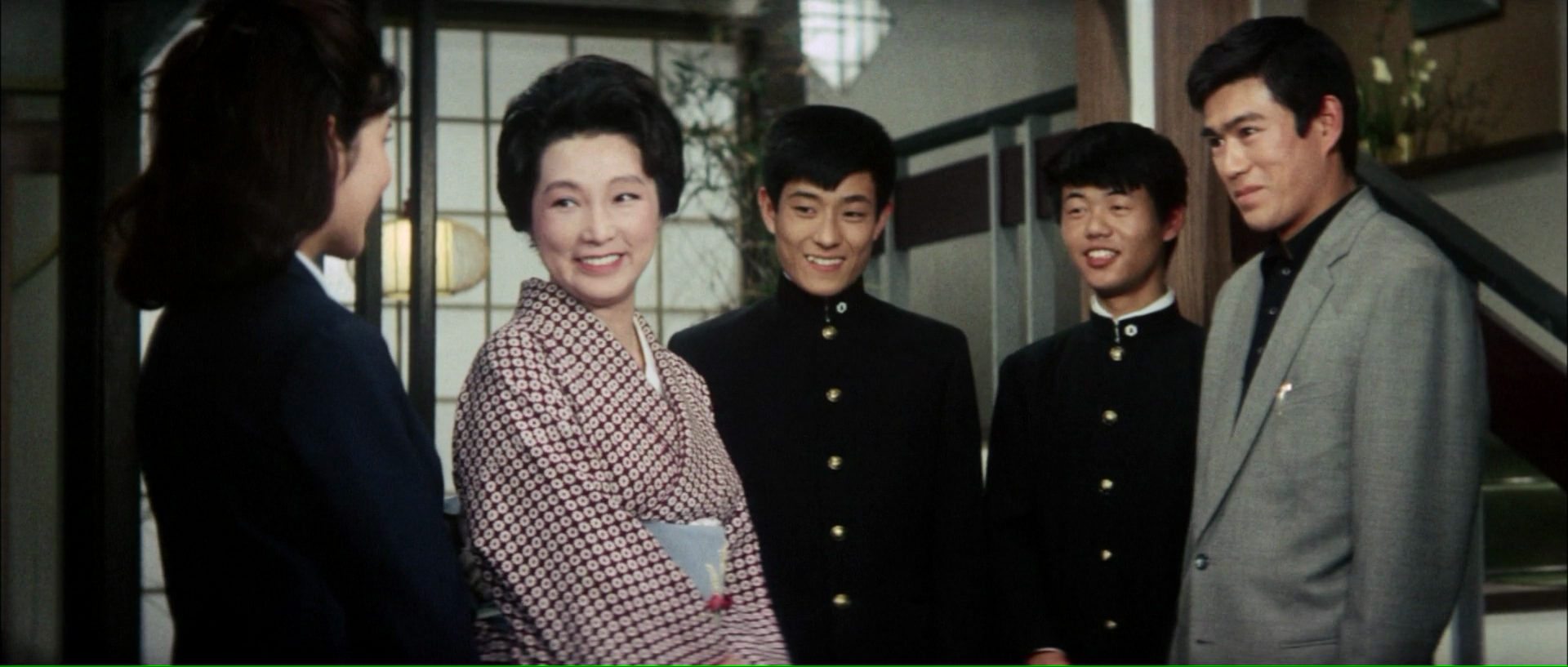











 Yasujiro Shimazu had been a pioneer of the “shomingeki” – naturalistic stories of ordinary lower middle class life, and his early career included several forays into the world of the “tendency film” which carried strong left-wing messages. By the late 1930s however his films have shifted upwards a little and often deal with the lives of the upper middle classes as they find themselves at another moment of transition during the turbulent militarist years. In contrast with many contemporary films, Shimazu’s may seem curiously apolitical but speak volumes solely through their subtlety and direct refusal to engage with the propagandist concerns of the ruling regime.
Yasujiro Shimazu had been a pioneer of the “shomingeki” – naturalistic stories of ordinary lower middle class life, and his early career included several forays into the world of the “tendency film” which carried strong left-wing messages. By the late 1930s however his films have shifted upwards a little and often deal with the lives of the upper middle classes as they find themselves at another moment of transition during the turbulent militarist years. In contrast with many contemporary films, Shimazu’s may seem curiously apolitical but speak volumes solely through their subtlety and direct refusal to engage with the propagandist concerns of the ruling regime. 
