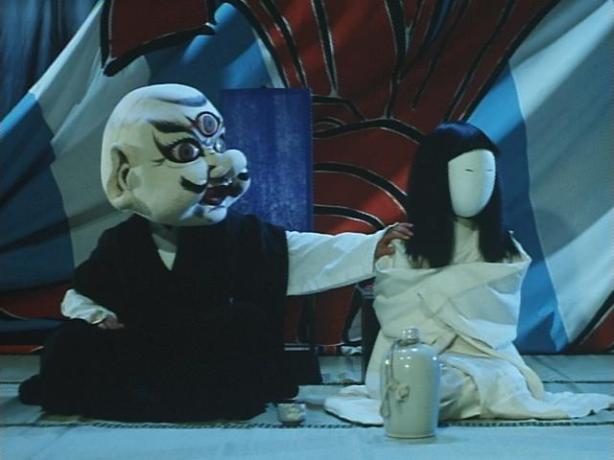
“How could you do this to me?” asks a wandering ghost in Masaki Mori’s 1959 Shintoho kaidan Ghosts of Kagami Pond (怪談鏡ケ淵, Kaidan Kagami-ga-fuchi). Based on a story by Kozo Hayama, Mori’s supernatural morality tale is in many ways fairly typical for the genre save that the vengeance wreaked by the wronged spirit is extremely targeted rather than the sometimes indiscriminate curses aimed more at a corrupt society than the figures directly responsible for the death and mistreatment inflicted on the now wrathful ghost.
The good-hearted hero, Yasujiro (Shozaburo Date), was forced to move to Edo after his father fell into disgrace with the Shogunate authorities and is grateful to have been taken in by the owner of kimono shop Ejimaya. However, his presence is intensely resented by veteran employee Kinbei (Joji Ohara) who had been expecting to inherit the business. Overhearing the boss, Jiemon (Hiroshi Hayashi), and his wife (Fumiko Miyata) discussing a possible marriage between Yasujiro and his childhood friend Kiku (Noriko Kitazawa) reunited by chance in the city, Kinbei realises that he intends to make Yasujiro his heir and hatches a plan to ensure that doesn’t happen beginning with selling Kiku’s sister Sato (Reiko Seto) a knock off wedding kimono that tears during the ceremony leading her intended’s family to cancel the marriage entirely leaving Sato a shamed woman in an impossible situation. Wandering the streets in despair intending to throw herself into Kagami Pond and thereafter become a vengeful ghost cursing the house of Ejimaya, Sato encounters Kinbei again and is killed in the ensuing struggle only to tumble into Kagami Pond sinking without trace.
“No one ever floats up out of there” Kinbei later insists suggesting the pond as a possible dumping ground for additional bodies of which there are a fair few. As kaidan villains go, Kinbei is of the one note variety in simply being evil for no particular reason the only justifications offered for his ill conduct being his previous devotion to the kimono store and the fear that all his hard work will go to waste if Yasujiro is allowed to inherit. Even so, this seems disingenuous given an early scene in which an angry customer brings a kimono back complaining of shoddy work and suggesting she’s been fobbed off with a substandard product. Kinbei blames the whole thing on new employee Yasujiro though it later seems clear that he probably sold her a cheap kimono and pocketed the difference in price.
He even goes so far as to mug Yasujiro in disguise, stealing 15 Ryo which he’d been transporting on behalf of the store attempting to sink his rival in debt. When Yasujiro’s disgraced father offers to sell a precious family sword to pay back Jiemon, Kinbei kills him too while 15 Ryo is also the amount for which he indentures Kiku to a brothel after framing her for adultery (illegal at the time) with the help of his sex worker co-conspirator Naka (Keiko Hamano) who bumps off Jiemon’s wife and quickly takes her place. Jiemon, who had previously been kind and fatherly insisting that Yasujiro and Kiku are like his own children to him, undergoes an unexplained and abrupt change of character becoming cruel and greedy, loaning money to another store holder in the assumption he won’t be able to pay it back in order to get his hands on his business and eventually party to all of Kinbei’s scheming little realising he most likely intends to bump him off too after he’s married Naka so that they will have full control of the business.
Kinbei is occasionally haunted by the rising ghost of Sato who chillingly repeats the phrase “How could you do this to me?” but carries on with his dastardly deeds anyway. As in most kaidan tales, she cannot hurt him directly but leads him to hurt himself by causing him to hallucinate, as do the ghosts of Yasujiro’s dad and the storeowner eventually calling him towards Kagami Pond and his watery fate. Some disjointed storytelling aside, the introduction of a potential ghost cat for example is never followed up, Ghosts of Kagami Pond is a fairly typical B-movie kaidan running a tight 60 minutes even if the effects and supernatural imagery are perhaps muted in comparison with Shintoho’s similarly themed ghostly morality tales.
Clip (no subtitles)






 No ghosts! That’s one of the big rules when it comes to the Chinese censors, but then these “ghosts” are not quite what they seem and belong to the pre-communist era when the people were far less enlightened than they are now. One of the few directors brave enough to tackle horror in China, Raymond Yip Wai-man goes for the gothic in this Phantom of the Opera inspired tale of love and the supernatural set in bohemian ‘30s Shanghai, Phantom of the Theatre (魔宫魅影, Mó Gōng Mèi Yǐng). As expected, the thrills and chills remain mild as the ghostly threat edges closer to its true role as metaphor in a revenge tale that is in perfect keeping with the melodrama inherent in the genre, but the full force of its tragic inevitability gets lost in the miasma of awkward CGI and theatrical artifice.
No ghosts! That’s one of the big rules when it comes to the Chinese censors, but then these “ghosts” are not quite what they seem and belong to the pre-communist era when the people were far less enlightened than they are now. One of the few directors brave enough to tackle horror in China, Raymond Yip Wai-man goes for the gothic in this Phantom of the Opera inspired tale of love and the supernatural set in bohemian ‘30s Shanghai, Phantom of the Theatre (魔宫魅影, Mó Gōng Mèi Yǐng). As expected, the thrills and chills remain mild as the ghostly threat edges closer to its true role as metaphor in a revenge tale that is in perfect keeping with the melodrama inherent in the genre, but the full force of its tragic inevitability gets lost in the miasma of awkward CGI and theatrical artifice.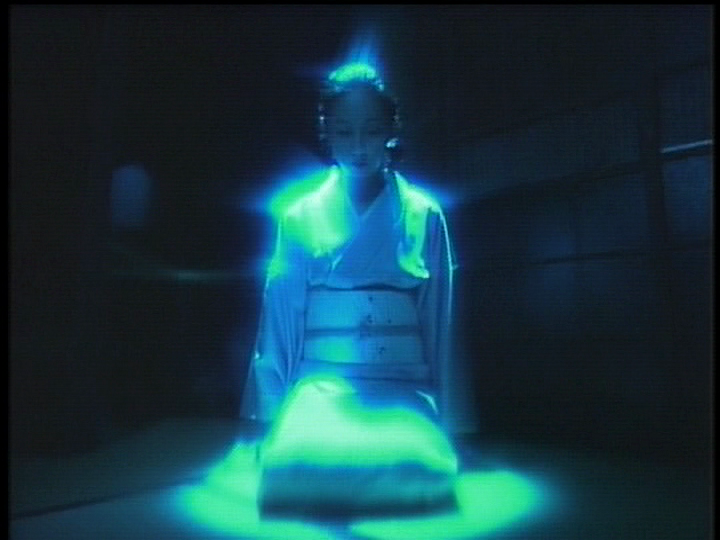 Akio Jissoji had a wide ranging career which encompassed everything from the Buddhist trilogy of avant-garde films he made for ATG to the Ultraman TV show. Post-ATG, he found himself increasingly working in television but aside from the children’s special effects heavy TV series, Jissoji also made time for a number of small screen movies including Blue Lake Woman (青い沼の女, Aoi Numa no Onna), an adaptation of a classic story from Japan’s master of the ghost story, Kyoka Izumi. Unsettling and filled with surrealist imagery, Blue Lake Woman makes few concessions to the small screen other than in its slightly lower production values.
Akio Jissoji had a wide ranging career which encompassed everything from the Buddhist trilogy of avant-garde films he made for ATG to the Ultraman TV show. Post-ATG, he found himself increasingly working in television but aside from the children’s special effects heavy TV series, Jissoji also made time for a number of small screen movies including Blue Lake Woman (青い沼の女, Aoi Numa no Onna), an adaptation of a classic story from Japan’s master of the ghost story, Kyoka Izumi. Unsettling and filled with surrealist imagery, Blue Lake Woman makes few concessions to the small screen other than in its slightly lower production values. Nobuhiko Obayashi is no stranger to a ghost story whether literal or figural but never has his pre-occupation with being pre-occupied about the past been more delicately expressed than in his 1988 horror-tinged supernatural adventure, The Discarnates (異人たちとの夏, Ijintachi to no Natsu). Nostalgia is a central pillar of Obayashi’s world, as drenched in melancholy as it often is, but it can also be pernicious – an anchor which pins a person in a certain spot and forever impedes their progress.
Nobuhiko Obayashi is no stranger to a ghost story whether literal or figural but never has his pre-occupation with being pre-occupied about the past been more delicately expressed than in his 1988 horror-tinged supernatural adventure, The Discarnates (異人たちとの夏, Ijintachi to no Natsu). Nostalgia is a central pillar of Obayashi’s world, as drenched in melancholy as it often is, but it can also be pernicious – an anchor which pins a person in a certain spot and forever impedes their progress. The Peony Lantern (牡丹燈籠, Kaidan Botan Doro) has gone by many different names in its English version – The Bride from Hades, The Haunted Lantern, Ghost Beauty, and My Bride is a Ghost among various others, but whatever the title of the tale it remains one of the best known ghost stories of Japan. Originally inspired by a Chinese legend, the story was adapted and included in a popular Edo era collection of supernatural tales, Otogi Boko (Hand Puppets), removing much of the original Buddhist morality tale in the process. In the late 19th century, the Peony Lantern also became one of the earliest standard rakugo texts and was then collected and translated by Lafcadio Hearn though he drew his inspiration from a popular kabuki version. As is often the case, it is Hearn’s version which has become the most common.
The Peony Lantern (牡丹燈籠, Kaidan Botan Doro) has gone by many different names in its English version – The Bride from Hades, The Haunted Lantern, Ghost Beauty, and My Bride is a Ghost among various others, but whatever the title of the tale it remains one of the best known ghost stories of Japan. Originally inspired by a Chinese legend, the story was adapted and included in a popular Edo era collection of supernatural tales, Otogi Boko (Hand Puppets), removing much of the original Buddhist morality tale in the process. In the late 19th century, the Peony Lantern also became one of the earliest standard rakugo texts and was then collected and translated by Lafcadio Hearn though he drew his inspiration from a popular kabuki version. As is often the case, it is Hearn’s version which has become the most common. Time is an ocean, but it ends at the shore. Kiyoshi Kurosawa neatly reverses Dylan’s poetic phrasing as his shoreline is less a place of endings but of beginnings or at least a representation of the idea that every beginning is born from the death of that which preceded it. Adapted from a novel by Kazumi Yumoto, Journey to the Shore (岸辺の旅, Kishibe no Tabi) takes its grief stricken, walking dead heroine on a long journey of the soul until she can finally put to rest a series of wandering ghosts and begin to live once again, albeit at her own tempo.
Time is an ocean, but it ends at the shore. Kiyoshi Kurosawa neatly reverses Dylan’s poetic phrasing as his shoreline is less a place of endings but of beginnings or at least a representation of the idea that every beginning is born from the death of that which preceded it. Adapted from a novel by Kazumi Yumoto, Journey to the Shore (岸辺の旅, Kishibe no Tabi) takes its grief stricken, walking dead heroine on a long journey of the soul until she can finally put to rest a series of wandering ghosts and begin to live once again, albeit at her own tempo. Kwaidan (怪談) is something of an anomaly in the career of the humanist director Masaki Kobayashi, best known for his wartime trilogy The Human Condition. Moving away from the naturalistic concerns that had formed the basis of his earlier career, Kwaidan takes a series of ghost stories collected by the foreigner Lafcadio Hearn and gives them a surreal, painterly approach that’s somewhere between theatre and folktale.
Kwaidan (怪談) is something of an anomaly in the career of the humanist director Masaki Kobayashi, best known for his wartime trilogy The Human Condition. Moving away from the naturalistic concerns that had formed the basis of his earlier career, Kwaidan takes a series of ghost stories collected by the foreigner Lafcadio Hearn and gives them a surreal, painterly approach that’s somewhere between theatre and folktale.